Home > Press > Relay race with single atoms: New ways of manipulating matter
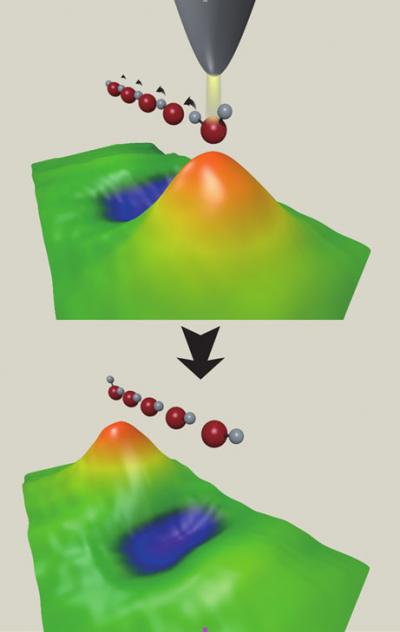 |
| This is an illustration of the atom relay process.
Credit: H. Okuyama |
Abstract:
Thanks to a collaboration between scientists in San Sebastian and Japan, a relay reaction of hydrogen atoms at a single-molecule level has been observed in real-space. This way of manipulating matter could open up new ways to exchange information between novel molecular devices in future electronics. Dr. Thomas Frederiksen, presently working in the Donostia International Physics Center (DIPC) is one of the scientists that has participated in this research project. The results have been published in the prestigious journal Nature Materials.
Relay race with single atoms: New ways of manipulating matter
San Sebastian, Spain | Posted on January 5th, 2012An athletic relay race is a competition where each member of a team sprints a short distance with the baton before passing it onwards to the next team member. This collective way of transporting something rapidly along a well-defined track is not only a human activity and invention - a similar relay mechanism, often refered to as structural diffusion, exists at the atomic scale that facilitate transport of hydrogen atoms and protons in hydrogen bonded networks, such as liquid water, biological systems, functional compounds, etc. However, direct visualization of this important transfer process in these situations is extremely difficult because of the highly complex environments.
Scientists in San Sebastian and Japan discovered that the relay reaction also occurs in well-defined molecular chains assembled on a metal surface. This new setup allowed the researchers to gain insight into the relay reactions at the level of single atoms and visualize the process using a scanning tunneling microscope (STM). By sending a pulse of electrons through a water molecule at one end of the chain, hydrogen atoms propagate one by one along the chain like dominoes in motion. The result is that a hydrogen atom has been transferred from one end to the other via the relay mechanism. The demonstrated control of the atom transfer along these molecular chains not only sheds new insight on a fundamental problem. It could also open up new ways to exchange information between novel molecular devices in future electronics by passing around hydrogen atoms.
T. Kumagai, A. Shiotari, H. Okuyama, S. Hatta, T. Aruga, I. Hamada, T. Frederiksen, and H. Ueba , H-atom Relay Reactions in Real Space, Nature Materials, DOI: 10.1038/NMAT3176.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aitziber Lasa
34-943-363-040
Copyright © Elhuyar Fundazioa
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








