Home > Press > A starring role for graphene: Rice University's functionalized graphene oxide plays part in next-generation oil-well drilling fluids
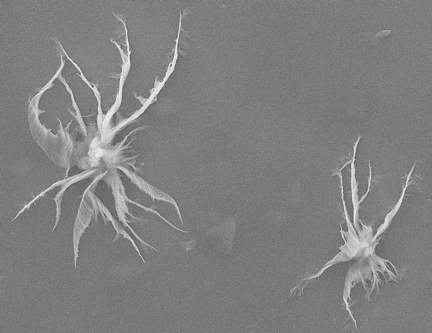 |
| Microscopic, star-shaped flakes of functionalized graphene oxide plug holes in pores in a test of the material's ability to serve as a filter cake in fluids used to drill oil wells. The single-atom-thick flakes of treated carbon are pliable but among the strongest materials known. (Credit Tour Group/Rice University) |
Abstract:
Graphene's star is rising as a material that could become essential to efficient, environmentally sound oil production. Rice University researchers are taking advantage of graphene's outstanding strength, light weight and solubility to enhance fluids used to drill oil wells.
A starring role for graphene: Rice University's functionalized graphene oxide plays part in next-generation oil-well drilling fluids
Houston, TX | Posted on December 8th, 2011The Rice University lab of chemist James Tour and scientists at M-I SWACO, a Texas-based supplier of drilling fluids and subsidiary of oil-services provider Schlumberger, have produced functionalized graphene oxide to alleviate the clogging of oil-producing pores in newly drilled wells.
The patented technique took a step closer to commercialization with the publication of new research this month in the American Chemical Society journal Applied Materials and Interfaces. Graphene is a one-atom-thick sheet of carbon that won its discoverers a Nobel Prize last year.
Rice's relationship with M-I SWACO began more than two years ago when the company funded the lab's follow-up to research that produced the first graphene additives for drilling fluids known as muds. These fluids are pumped downhole as part of the process to keep drill bits clean and remove cuttings. With traditional clay-enhanced muds, differential pressure forms a layer on the wellbore called a filter cake, which both keeps the oil from flowing out and drilling fluids from invading the tiny, oil-producing pores.
When the drill bit is removed and drilling fluid displaced, the formation oil forces remnants of the filter cake out of the pores as the well begins to produce. But sometimes the clay won't budge, and the well's productivity is reduced.
The Tour Group discovered that microscopic, pliable flakes of graphene can form a thinner, lighter filter cake. When they encounter a pore, the flakes fold in upon themselves and look something like starfish sucked into a hole. But when well pressure is relieved, the flakes are pushed back out by the oil.
All that was known two years ago. Since then, Tour and a research team led by Dmitry Kosynkin, a
former Rice postdoctoral associate and now a petroleum engineer at Saudi Aramco, have been fine-tuning the materials.
They found a few issues that needed to be dealt with. First, pristine graphene is hard to disperse in water, so it is unsuitable for water-based muds. Graphene oxide (GO) turned out to be much more soluble in fresh water, but tended to coagulate in saltwater, the basis for many muds.
The solution was to "esterify" GO flakes with alcohol. "It's a simple, one-step reaction," said Tour, Rice's T.T. and W.F. Chao Chair in Chemistry as well as a professor of mechanical engineering and materials science and of computer science. "Graphene oxide functionalized with alcohol works much better because it doesn't precipitate in the presence of salts. There's nothing exotic about it."
In a series of standard American Petroleum Institute tests, the team found the best mix of functionalized GO to be a combination of large flakes and powdered GO for reinforcement. A mud with 2 percent functionalized GO formed a filter cake an average of 22 micrometers wide -- substantially smaller than the 278-micrometer cake formed by traditional muds. GO blocked pores many times smaller than the flakes' original diameter by folding.
Aside from making the filter cake much thinner, which would give a drill bit more room to turn, the Rice mud contained less than half as many suspended solids; this would also make drilling more efficient as well as more environmentally friendly. Tour and Andreas Lüttge, a Rice professor of Earth science and chemistry, reported last year that GO is reduced to graphite, the material found in pencil lead and a natural mineral, by common bacteria.
"The most exciting aspect is the ability to modify the GO nanoparticle with a variety of functionalities," said James Friedheim, corporate director of fluids research and development at M-I SWACO and a co-author of the research. "Therefore we can 'dial in' our application by picking the right organic chemistry that will suit the purpose. The trick is just choosing the right chemistry for the right purpose."
"There's still a lot to be worked out," Tour said. "We're looking at the rheological properties, the changes in viscosity under shear. In other words, we want to know how viscous this becomes as it goes through a drill head, because that also has implications for efficiency."
Muds may help graphene live up to its commercial promise, Tour said. "Everybody thinks of graphene in electronics or in composites, but this would be a use for large amounts of graphene, and it could happen soon," he said.
Friedheim agreed. "With the team we currently have assembled, Jim Tour's group and some development scientists at M-I SWACO, I am confident that we are close to both technical and commercial success."
Other authors of the paper are Rice graduate student Gabriel Ceriotti, former Rice research associates Kurt Wilson and Jay Lomeda, and M-I SWACO researchers Jason Scorsone and Arvind Patel.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation's top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is known for its "unconventional wisdom." With 3,708 undergraduates and 2,374 graduate students, Rice's undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is less than 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice has been ranked No. 1 for best quality of life multiple times by the Princeton Review and No. 4 for "best value" among private universities by Kiplinger's Personal Finance. To read "What they're saying about Rice," go to www.rice.edu/nationalmedia/Rice.pdf.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Breakthrough in proton barrier films using pore-free graphene oxide: Kumamoto University researchers achieve new milestone in advanced coating technologies September 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








