Home > Press > Rare Coupling of Magnetic and Electric Properties in a Single Material: New multiferroic mechanism could lead to next-generation memory and sensing devices
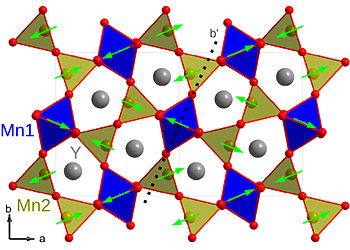 |
| The crystal structure of YMn2O5, which is made of yttrium, manganese, and oxygen. The oxygen atoms are shown in red and the yttrium atoms are gray. The magnetic moments on the manganese are shown as arrows. Ferroelectric polarization occurs between the oxygen and manganese atoms. |
Abstract:
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy's Brookhaven National Laboratory have observed a new way that magnetic and electric properties - which have a long history of ignoring and counteracting each other - can coexist in a special class of metals. These materials, known as multiferroics, could serve as the basis for the next generation of faster and energy-efficient logic, memory, and sensing technology.
Rare Coupling of Magnetic and Electric Properties in a Single Material: New multiferroic mechanism could lead to next-generation memory and sensing devices
Upton, NY | Posted on July 25th, 2011The researchers, who worked with colleagues at the Leibniz Institute for Solid State and Materials Research in Germany, published their findings online in Physical Review Letters on July 25, 2011.
Ferromagnets are materials that display a permanent magnetic moment, or magnetic direction, similar to how a compass needle always points north. They assist in a variety of daily tasks, from sticking a reminder to the fridge door to storing information on a computer's hard drive. Ferroelectrics are materials that display a permanent electric polarization - a set direction of charge - and respond to the application of an electric field by switching this direction. They are commonly used in applications like sonar, medical imaging, and sensors.
"In principle, the coupling of an ordered magnetic material with an ordered electric material could lead to very useful devices," said Brookhaven physicist Stuart Wilkins, one of the paper's authors. "For instance, one could imagine a device in which information is written by application of an electric field and read by detecting its magnetic state. This would make a faster and much more energy-efficient data storage device than is available today."
But multiferroics - magnetic materials with north and south poles that can be reversed with an electric field - are rare in nature. Ferroelectricity and magnetism tend to be mutually exclusive and interact weakly with each other when they coexist.
Most models used by physicists to describe this coupling are based on the idea of distorting the atomic arrangement, or crystal lattice, of a magnetic material, which can result in an electric polarization.
Now, scientists have found a new way that electric and magnetic properties can be coupled in a material. The group used extremely bright beams of x-rays at Brookhaven's National Synchrotron Light Source (NSLS) to examine the electronic structure of a particular metal oxide made of yttrium, manganese, and oxygen. They determined that the magnetic-electric coupling is caused by the outer cloud of electrons surrounding the atom.
"Previously, this mechanism had only been predicted theoretically and its existence was hotly debated," Wilkins said.
In this particular material, the manganese and oxygen electrons mix atomic orbitals in a process that creates atomic bonds and keeps the material together. The researchers' measurements show that this process is dependent upon the magnetic structure of the material, which in this case, causes the material to become ferroelectric, i.e. have an electric polarization. In other words, any change in the material's magnetic structure will result in a change in direction of its ferroelectric state. By definition, that makes the material a multiferroic.
"What is especially exciting is that this result proves the existence of a new coupling mechanism and provides a tool to study it," Wilkins said.
The researchers used a new instrument at NSLS designed to answer key questions about many intriguing classes of materials such as multiferroics and high-temperature superconductors, which conduct electricity without resistance. The instrument, developed by Wilkins and Brookhaven engineers D. Scott Coburn, William Leonhardt, and William Schoenig, will ultimately be moved to the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a state-of-the-art machine currently under construction. NSLS-II will produce x-rays 10,000 times brighter than at NSLS, enabling studies of materials' properties at even higher resolution.
This work was supported by the U.S. Department of Energy Office of Science.
####
About Brookhaven National Laboratory
One of ten national laboratories overseen and primarily funded by the Office of Science of the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), Brookhaven National Laboratory conducts research in the physical, biomedical, and environmental sciences, as well as in energy technologies and national security. Brookhaven Lab also builds and operates major scientific facilities available to university, industry and government researchers. Brookhaven is operated and managed for DOE's Office of Science by Brookhaven Science Associates, a limited-liability company founded by the Research Foundation of State University of New York on behalf of Stony Brook University, the largest academic user of Laboratory facilities, and Battelle, a nonprofit, applied science and technology organization.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Kendra Snyder
631-344-8191
or
Peter Genzer
631-344-3714
Copyright © Brookhaven National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The scientific paper is available at:
The scientific paper is available at:
![]() Visit Brookhaven Lab's electronic newsroom for links, news archives, graphics, and more at:
Visit Brookhaven Lab's electronic newsroom for links, news archives, graphics, and more at:
![]() Follow Brookhaven Lab on Twitter:
Follow Brookhaven Lab on Twitter:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Superconductivity
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








