Home > Press > New method manipulates particles for sensors, crime scene testing
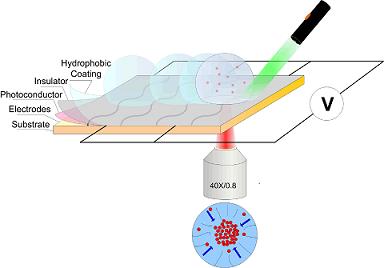 |
| This diagram depicts the design of a new "hybrid optoelectric" device. The device uses a tightly focused infrared laser beam to position tiny particles, such as viruses and bacteria, onto a sensor. (Han-Sheng Chuang/Purdue University Birck Nanotechnology Center) |
Abstract:
Researchers at Purdue University have developed a potential new tool for medical diagnostics, testing food and water for contamination, and crime-scene forensics.
By Emil Venere
New method manipulates particles for sensors, crime scene testing
West Lafayette, IN | Posted on June 8th, 2010The technique uses a combination of light and electric fields to position droplets and tiny particles, such as bacteria, viruses and DNA, which are contained inside the drops.
Other methods using either light or electric fields separately are able to position droplets or the particles they contain, but the new "hybrid optoelectric" device is able to do both, making it potentially practical for sensors and industrial processes, said mechanical engineering doctoral student Aloke Kumar.
Ordinarily, the particles inside droplets are detected when they randomly fall on a sensor's surface. However, the new method could improve sensor efficiency by actively moving particles to specific regions on an electronic chip for detection or analysis.
"This new hybrid technique is universal in the sense that we can manipulate a range of droplet and particle sizes, going all the way from microliter drops to particles a few nanometers long," said Steven T. Wereley, a professor of mechanical engineering who is working with Kumar.
The method offers promise for future "lab-on-a-chip" technology, using electronic chips to analyze biological samples for medical and environmental applications. Sensors based on the technique could make possible a new class of chemical analyses, or assays, with point-of-care devices in a doctor's office or hospitals.
Such sensors might be used to quickly analyze blood, urine and other bodily fluids for a range of applications, including drug screening; paternity testing; detecting coronary artery disease, tumors and various inherited diseases including cystic fibrosis; and detecting infectious diseases and bacteria, viruses and fungi that are difficult to culture using conventional laboratory methods.
"This technique also would be good for DNA tests, such as those used on the TV program 'CSI,' to identify crime suspects using only a small blood sample," Wereley said. "The idea is to use a chip to quickly carry out laboratory procedures called polymerase chain reaction and capillary electrophoresis. The new technology also should be good for testing food and water for pathogens such as E. coli or salmonella."
Critical to the technology are electrodes made of indium tin oxide, a transparent and electrically conductive material commonly used in consumer electronics for touch-screen displays. Liquid drops are positioned on the electrodes, and the infrared laser heats up both the electrodes and the droplets. Then electric fields in the electrodes cause the heated liquid to produce a "microfluidic vortex" of circulating liquid. This vortex enables researchers to position the particles in the circulating liquid by moving the infrared laser. The particles accumulate only where the laser is shined.
"Sensors are one of the immediate applications of this technology," said Kumar, who may continue the work as a postdoctoral researcher at the Oak Ridge National Laboratories, where he will complete a two-year Eugene Wigner Fellowship starting this month. "We should be able to improve the efficiency of sensors at least 10 times."
Findings were detailed in a research paper appearing June 1 in the journal Langmuir. The paper was written by Kumar, Wereley and former Purdue doctoral student Han-Sheng Chuang, now a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Pennsylvania. The research is based at the Birck Nanotechnology Center at Purdue's Discovery Park.
Purdue has filed a U.S. patent application on the design.
The technique might be used to manufacture sensors and other devices by modifying a phenomenon called the coffee-ring effect, which causes residue to form when liquid evaporates. Because the particles in the residue form only where the infrared laser shines, the procedure might be used to precisely position particles to create structures and circuits for biosensors and electronics.
"We have successfully used this technique to create spatially controlled microassemblies, and we hope that this would interest other research groups looking into the coffee-ring effect," Kumar said.
The work has been supported with funding from the National Science Foundation and the Micro/Nano Fluidics Fundamentals Focus (MF3) Center at the University of California, Irvine.
ABSTRACT
Dynamic Manipulation by Light and Electric Fields: Micrometer Particles to Microliter Droplets
Aloke Kumar,† Han-Sheng Chuang,†,‡ and Steven T. Wereley
†Birck Nanotechnology Center and School of Mechanical Engineering, Purdue University
‡Mechanical Engineering and Applied Mechanics, University of Pennsylvania
We demonstrate a new hybrid optoelectric technique that can manipulate objects across several length scales. The technique leverages a variety of different physical mechanisms to achieve the dynamic manipulation of droplets and also the in situ concentration of colloidal particles suspended in the droplets. Various physical mechanisms such as optoelectrowetting, electrothermal flows, and ac electroosmosis are leveraged through different modes of operation of the device. Each operational mode, which is activated through the proper combination of an applied ac bias and the illumination used, is characterized by the ability to manipulate objects on a certain length scale. We also demonstrate that the device lends itself to the active control of microstructure patterns that emerge from a droplet evaporation process.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Writer:
Emil Venere
(765) 494-4709
Sources:
Steven T. Wereley
765-494-5624
Aloke Kumar
765-586-7884
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Law enforcement/Anti-Counterfeiting/Security/Loss prevention
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Food/Agriculture/Supplements
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
SMART researchers pioneer first-of-its-kind nanosensor for real-time iron detection in plants February 28th, 2025
![]() Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Silver nanoparticles: guaranteeing antimicrobial safe-tea November 17th, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








