Home > Press > Purdue simulation to help merge molecules with silicon electronics
Abstract:
"Molecular electronic" devices for future computers and advanced sensors
Purdue simulation to help merge molecules with silicon electronics
August 16, 2005
Engineers at Purdue University have created a nanotech simulation tool that shows how current flows between silicon atoms and individual molecules to help researchers design "molecular electronic" devices for future computers and advanced sensors.
Molecular electronics could make it possible to manufacture hardware by "growing" circuits and devices in layers that may "self-assemble," similar to the growth of structures in living organisms. Devices for a variety of applications might be fabricated using techniques based on chemical attractions rather than the complex, expensive processes now used to etch electronic circuits.
One challenge, however, in developing molecular electronics is to better understand how electricity is conducted between molecules and silicon contacts connecting various devices in a circuit, said Geng-Chiau Liang, a postdoctoral research assistant in Purdue's School of Electrical and Computer Engineering.
Researchers will be able to use the new simulation tool to see precisely how electrical conductivity changes depending on how molecules are connected to silicon, information that is critical to properly design the devices.
"I believe we might be one of the first theorists who have created a tool to show how electricity is conducted between molecules and silicon at the atomic level," said Avik Ghosh, a research scientist in electrical and computer engineering who worked with Liang.
Details about the simulation tool are appearing in the current issue (Aug. 12, Volume 95, Issue 7) of the journal Physical Review Letters. The paper was written by Liang and Ghosh. The research has been funded through two national centers based at Purdue's Discovery Park, the university's hub for interdisciplinary research.
Scientists and engineers are working to develop techniques for creating future computers, sensors and other devices that use molecules, such as proteins and DNA, instead of conventional electronic components. The concept may spawn new "biochips" that will use proteins in sensors for detecting contaminants and pollutants in the air and water and for analyzing the blood and biological samples.
"The idea is that molecules might be able to complement or supplement silicon," Ghosh said. "All traditional research in molecular electronics has focused on combining molecules with metal contacts, but we've been studying the interaction of molecules and silicon instead of metals because the computer industry is built on semiconductors, which is silicon."
Liang and Ghosh used the tool to show how current flows between silicon atoms and molecules called buckminsterfullerenes, or "buckyballs."
Named after architect R. Buckminster Fuller, who designed the geodesic dome, buckyballs are soccer-ball-shaped molecules containing 60 carbon atoms. A buckyball has a width of about 1 nanometer, or one-billionth of a meter, which is roughly 10 atoms wide.
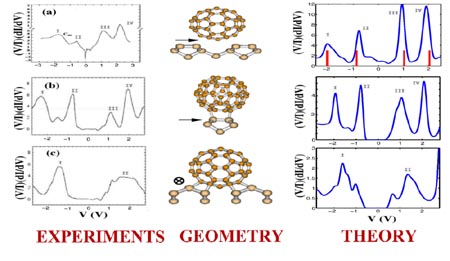
"This paper is a proof of concept showing that our theory is at a point that we can actually look at experiments and explain them quantitatively," Liang said. "We have shown how the conductance of electricity changes when you change the type of bond connecting buckyballs to silicon."
The researchers used their computational model to predict how electricity flows when buckyballs and silicon are connected in three ways. In one case, there is no chemical bond - the buckyball is simply sitting on top of the silicon. In another case, the molecule has been connected to silicon by annealing, or heating, the silicon. And in the third case, the buckyball is resting inside of a tiny pit, a natural defect existing in the silicon.
The model precisely plotted how conduction and voltage changed in the three types of connections, and those predictions agreed with experimental data from other researchers who measured the actual changes in current flow in laboratories.
"Because our predictions agreed with actual experimental data, we know they are accurate," Ghosh said. "This means you can use the model to give theoretical guidance to experiments instead of using strictly a trial-and-error approach."
Together with Supriyo Datta, the Thomas Duncan Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering at Purdue, and his students, Liang and Ghosh developed the mathematical theory on which the model is based. The researchers used a Purdue supercomputer to develop and test the simulation.
The Purdue engineers used buckyballs in their simulation because the molecules are well-known in the scientific community and data are readily available. The tool, however, could be used to simulate conduction using any molecule connected to silicon.
"Researchers want to know what kind of molecule can provide specific conduction characteristics, and they can substitute other molecules for buckyballs," Liang said. "What we can now do is theoretically explain the experiments in quantitative detail, which is really important for any technology.
"To do this, you must have an atomistic understanding of current flow - basically, how does electricity conduct at the atomic level."
The research is ongoing and has been supported by the Network for Computational Nanotechnology, funded by the National Science Foundation and directed by Mark Lundstrom, Purdue's Scifres Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering; the Semiconductor Research Corporation; the Defense University Research Initiative on Nanotechnology, which is supported by the U.S. Army Research Office; and the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency.
Writer: Emil Venere, (765) 494-4709, venere@purdue.edu
Sources: Geng-Chiau Liang, (765) 494-9050, liangg@purdue.edu
Avik Ghosh, (765) 494-9023, (Cell Phone) (765) 532-0538, ghosha@ecn.purdue.edu (After Aug. 25, use ag7rq@virginia.edu)
Note to Journalists: An electronic copy of the research paper is available from Emil Venere.
Contact:
Emil Venere
(765) 494-4709
venere@purdue.edu
Copyright © Purdue University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Self Assembly
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Tools
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
![]() Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||