Home > Press > Engineers develop new magnetic ink to print self-healing devices that heal in record time
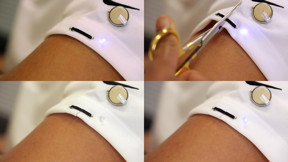 |
| Nanoengineers printed a self-healing circuit on the sleeve of a T-shirt and connected it with an LED light and a coin battery. The researchers then cut the circuit and the fabric it was printed on. At that point, the LED turned off. But then within a few seconds it started turning back on as the two sides of the circuit came together again and healed themselves, restoring conductivity. CREDIT Jacobs School of Engineering/UC San Diego |
Abstract:
A team of engineers at the University of California San Diego has developed a magnetic ink that can be used to make self-healing batteries, electrochemical sensors and wearable, textile-based electrical circuits.
Engineers develop new magnetic ink to print self-healing devices that heal in record time
San Diego, CA | Posted on November 7th, 2016The key ingredient for the ink is microparticles oriented in a certain configuration by a magnetic field. Because of the way they're oriented, particles on both sides of a tear are magnetically attracted to one another, causing a device printed with the ink to heal itself. The devices repair tears as wide as 3 millimeters--a record in the field of self-healing systems.
Researchers detail their findings in the Nov. 2 issue of Science Advances.
"Our work holds considerable promise for widespread practical applications for long-lasting printed electronic devices," said Joseph Wang, director of the Center for Wearable Sensors and chair of the nanoengineering department at UC San Diego.
Existing self-healing materials require an external trigger to kick start the healing process. They also take anywhere between a few minutes to several days to work. By contrast, the system developed by Wang and colleagues doesn't require any outside catalyst to work. Damage is repaired within about 50 milliseconds (0.05 seconds).
Engineers used the ink to print batteries, electrochemical sensors and wearable, textile-based electrical circuits (see video). They then set about damaging these devices by cutting them and pulling them apart to create increasingly wide gaps. Researchers repeatedly damaged the devices nine times at the same location. They also inflicted damage in four different places on the same device. The devices still healed themselves and recovered their function while losing a minimum amount of conductivity.
For example, nanoengineers printed a self-healing circuit on the sleeve of a T-shirt and connected it with an LED light and a coin battery. The researchers then cut the circuit and the fabric it was printed on. At that point, the LED turned off. But then within a few seconds it started turning back on as the two sides of the circuit came together again and healed themselves, restoring conductivity.
"We wanted to develop a smart system with impressive self-healing abilities with easy-to-find, inexpensive materials," said Amay Bandodkar, one of the papers' first authors, who earned his Ph.D. in Wang's lab and is now a postdoctoral researcher at Northwestern University.
Fabrication
Wang's research group is a leader in the field of printed wearable sensors, so his team of nanoengineers naturally turned to ink as a starting point for their self-healing system.
Engineers loaded the ink with microparticles made of a type of magnet commonly used in research and made of neodymium, a soft, silvery metal. The particles' magnetic field is much larger than their individual size. This is the key to the ink's self-healing properties because the attraction between the particles leads to closing tears that are millimeters wide.
The particles also conduct electricity and are inexpensive. But they have poor electrochemical properties, making them difficult to use in the electrochemical devices, such as sensors, on their own. To remedy this problem, researchers added carbon black to the ink, a material commonly used to make batteries and sensors.
But researchers realized that the microparticles' magnetic fields, when in their natural configuration, canceled each other out, which robbed them of their healing properties. Engineers solved this by printing the ink in the presence of an external magnetic field, which ensured that the particles oriented themselves to behave as a permanent magnet with two opposite poles at the end of each printed device. When the device is cut in two, the two damaged pieces act as different magnets that attract each other and self-heal.
In the future, engineers envision making different inks with different ingredients for a wide range of applications. In addition, they plan to develop computer simulations to test different self-healing ink recipes in silico before trying them out in the lab.
###
"All-printed magnetically self-healing electrochemical devices" by Amay J. Bandodkar, Christian S. Lopez, Allibai Mohanan, Vinu Mohan, Lu Yin, Rajan Kumar, Joseph Wang. Bandodkar is now a postdoctoral fellow at Northwestern University. All other authors are affiliated with the Department of Nanoengineering at the Jacobs School of Engineering at UC San Diego. This work was supported by the NIH (award R21EB019698) and Advanced Research Projects Agency-Energy (award DE-AR0000535).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
IOANA PATRINGENARU
858-822-0899
Copyright © University of California, San Diego
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Wearable electronics
![]() Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
Breakthrough brings body-heat powered wearable devices closer to reality December 13th, 2024
![]() Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Beyond wires: Bubble technology powers next-generation electronics:New laser-based bubble printing technique creates ultra-flexible liquid metal circuits November 8th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
![]() Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Flexible electronics integrated with paper-thin structure for use in space January 17th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Textiles/Clothing
![]() Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
Protective equipment with graphene nanotubes meets the strictest ESD safety standards March 25th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
![]() Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Flexible material shows potential for use in fabrics to heat, cool July 3rd, 2020
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Printing/Lithography/Inkjet/Inks/Bio-printing/Dyes
![]() Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
Presenting: Ultrasound-based printing of 3D materials—potentially inside the body December 8th, 2023
![]() Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
Simple ballpoint pen can write custom LEDs August 11th, 2023
![]() Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
Disposable electronics on a simple sheet of paper October 7th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








