Home > Press > Chung-Ang University researchers develop novel DNA biosensor for early diagnosis of cervical cancer: The electrochemical sensor, made of a graphitic nano-onion/molybdenum disulfide nanosheet composite, detects human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 and HPV-18, with high specificity
 |
| Chung-Ang University researchers have developed a novel electrochemical nano-onion/molybdenum disulfide nanosheet composite-based DNA biosensor that efficiently and specifically detects human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 and HPV-18, enabling early diagnosis of cervical cancer. CREDIT Journal of Nanobiotechnology |
Abstract:
Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) has recently garnered attention among materials science researchers owing to its ability to form two-dimensional nanosheets like graphene. The nanosheets are created by the stacking of S–Mo–S layers interacting via Van der Waals interactions. Additionally, the unique structural, optical, thermal, and electrochemical properties of MoS2 have opened up multiple research avenues across several fields, including the development of biomolecule sensing and chemical detection platforms, optoelectronics, supercapacitors, and batteries.
Chung-Ang University researchers develop novel DNA biosensor for early diagnosis of cervical cancer: The electrochemical sensor, made of a graphitic nano-onion/molybdenum disulfide nanosheet composite, detects human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 and HPV-18, with high specificity
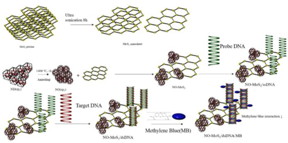
Seoul, Republic of Korea | Posted on September 8th, 2023Traditionally, carbon nanostructures have been employed as an immobilization platform for DNA. In order to substitute carbon with MoS2 as an effective electrochemical DNA sensor, the electrical conductivity of MoS2 needs to be improved considerably. Against this backdrop, Associate Professor Eunah Kang and Mr. Youngjun Kim from the School of Chemical Engineering and Material Science at Chung-Ang University, Korea have recently come up with an elegant solution. The duo has developed an electrochemical DNA biosensor using a graphitic nano-onion/molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanosheet composite, which effectively detects human papillomavirus (HPV)-16 and HPV-18, and can serve as an early diagnosis of cervical cancer.
“Nano-onions possess graphitic sp2 structures and are derived from crystalline sp3 nanodiamonds via thermal annealing or laser irradiation,” explains Dr. Kang. Their breakthrough was published in Volume 21 of the Journal of Nanobiotechnology on 10 June 2023.
The researcher duo prepared the novel electrode surface for probing DNA chemisorption by enabling chemical conjugation between two functional groups: acyl bonds on the surfaces of functionalized nano-onions and amine groups present on the modified MoS2 nanosheets. Cyclic voltammetry experiments revealed that a 1:1 composite electrode had an improved rectangular shape compared to that of an MoS2 nanosheet electrode. “This indicated the amorphous nature of the nano-onions with curved carbon layers that facilitated an enhancement in electronic conductivity compared to MoS2 nanosheet alone,” highlights Dr. Kang.
Additionally, the duo measured the sensitivity of their novel electrochemical DNA biosensor device towards HPV-16 and HPV-18 by employing differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) technique in the presence of methylene blue (MB) as a redox indicator. Dr. Kang elaborates: “The DPV current peak was lowered after probe DNA chemisorption and target DNA hybridization. Since the hybridized DNA was double-stranded, it induced less effective MB electrostatic intercalation, resulting in a lower oxidation peak.”
The duo found that, compared to the MoS2 nanosheet electrode, the nano-onion/MoS2 nanosheet composite electrode attained higher current peaks, indicating a greater change in the differential peak. This was attributed to an enhanced conductive electron transfer owing to the nano-onion.
Notably, the target DNAs produced from HPV-16 and HPV-18 Siha and Hela cancer cell lines were detected by the proposed sensor effectively and with high specificity. Consequently, MoS2 nanosheets with improved electrical conductivity facilitated by complexation with nano-onions provides a suitable platform for developing effective and efficient electrochemical biosensors for the early diagnosis of a wide variety of ailments, including cervical cancer.
Furthermore, combining nano-onions or nanodiamonds with different organic biomaterials can facilitate chemical functionality, electron transfer conductivity, light absorption, and more. These, in turn, can lead to innovative disease sensing, targeted drug delivery systems, and biomedical imaging and diagnostics.
####
About Chung-Ang University
Chung-Ang University is a private comprehensive research university located in Seoul, South Korea. It was started as a kindergarten in 1916 and attained university status in 1953. It is fully accredited by the Ministry of Education of Korea. Chung-Ang University conducts research activities under the slogan of “Justice and Truth.” Its new vision for completing 100 years is “The Global Creative Leader.” Chung-Ang University offers undergraduate, postgraduate, and doctoral programs, which encompass a law school, management program, and medical school; it has 16 undergraduate and graduate schools each. Chung-Ang University’s culture and arts programs are considered the best in Korea.
Website: https://neweng.cau.ac.kr/index.do
About the author
Eunah Kang is an Associate Professor at the School of Chemical Engineering and Material Science at Chung-Ang University (CAU). She received her Ph.D. in Biomedical Engineering from Purdue University in 2007. Her group at CAU develops versatile approaches to drug delivery systems, sensors, and imaging theragnostic agents by designing complexes with new organic and inorganic materials. This includes combining nanodiamonds or nano-onions with common biopolymers and drug delivery carriers to enable innovative functions and applications in biomedicine.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Se-Jin Oh
Chung-Ang University
Office: 02-820-6614
Copyright © Chung-Ang University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Cancer
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Self-propelled protein-based nanomotors for enhanced cancer therapy by inducing ferroptosis June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Deciphering local microstrain-induced optimization of asymmetric Fe single atomic sites for efficient oxygen reduction August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








