Home > Press > Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance
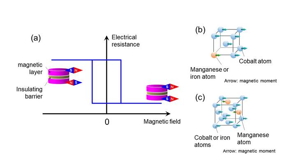 |
| (a) A schematic diagram of a tunnel magnetoresistive device and magnetoresistance. (b) A schematic diagram of the crystal of the metastable body-centered cubic cobalt-manganese alloy studied. (c) A schematic diagram of the face-centered cubic structure, which is one of the thermodynamically stable phases of cobalt-manganese alloys. CREDIT Shigemi Mizukamai and Tomohiro Ichinose |
Abstract:
A group of researchers from Tohoku University has unveiled a new material that exhibits enormous magnetoresistance, paving the way for developments in non-volatile magnetoresistive memory (MRAM).
Researchers discover materials exhibiting huge magnetoresistance
Sendai City, Japan | Posted on June 9th, 2023Today, the demand for advancements in hardware that can efficiently process large amounts of digital information and in sensors has never been greater, especially with governments deploying technological innovations to achieve smarter societies.
Much of this hardware and sensors rely on MRAM and magnetic sensors, and tunnel magnetoresistive devices make up the majority of such devices.
Tunnel magnetoresistive devices exploit the tunnel magnetoresistance effect to detect and measure magnetic fields. This is tied to the magnetization of ferromagnetic layers in magnetic tunnel junctions. When the magnets are aligned, a low resistance state is observed, and electrons can easily tunnel through the thin insulating barrier between them. When the magnets are not aligned, the tunneling of electrons becomes less efficient and leads to higher resistance. This change in resistance is expressed as the magnetoresistive ratio, a key figure in determining the efficiency of tunneling magnetoresistive devices. The higher the magnetoresistance ratio, the better the device is.
Current tunnel magnetoresistive devices comprise magnesium oxide and iron-based magnetic alloys, like iron-cobalt. Iron-based alloys have a body-centered cubic crystal structure in ambient conditions and exhibit a huge tunnel magnetoresistance effect in devices with a rock salt-type magnesium oxide.
There have been two notable studies using these iron-based alloys that produced magnetoresistive devices displaying high magnetoresistance ratios. The first in 2004 was by the National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology in Japan and IBM; and the second came in 2008, when researchers from Tohoku University reported on a magnetoresistance ratio exceeding 600% at room temperature, something that jumped to 1000% with temperatures near zero kelvin.
Since those breakthroughs, various institutes and companies have invested considerable effort in honing device physics, materials, and processes. Yet aside from iron-based alloys, only some Heusler-type ordered magnetic alloys have displayed such enormous magnetoresistance.
Dr. Tomohiro Ichinose and Professor Shigemi Mizukami from Tohoku University recently began exploring thermodynamically metastable materials to develop a new material capable of demonstrating similar magnetoresistance ratios. To do so, they focused on the strong magnetic properties of cobalt-manganese alloys, which have a body-centered cubic metastable crystal structure.
"Cobalt-manganese alloys have face-centered cubic or hexagonal crystal structures as thermodynamically stable phases. Because this stable phase exhibits weak magnetism, it has never been studied as a practical material for tunnel magnetoresistive devices," said Mizukami.
Back in 2020, the group reported on a device that used a cobalt-manganese alloy with metastable body-centered cubic crystal structure.
Using data science and/or high-throughput experimental methods, they built upon this discovery, and succeeded in obtaining huge magnetoresistance in devices by adding a small amount of iron to the metastable body-centered cubic cobalt-manganese alloy. The magnetoresistance ratio was 350% at room temperature and also exceeded 1000% at a low temperature. Additionally, the device fabrication employed the sputtering method and a heating process, something compatible with current industries.
"We have produced the third instance of a new magnetic alloy for tunneling magnetoresistive devices showing huge magnetoresistance, and it sets an alternative direction of travel for future improvements," adds Mizukami.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Public Relations
Tohoku University
Copyright © Tohoku University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








