Home > Press > Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments
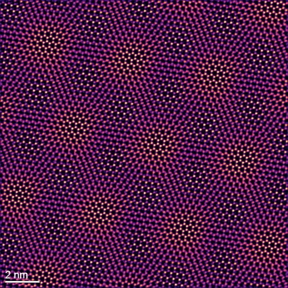 |
| Yu-Tsun Shao and David Muller/Provided A transmission electron microscope image shows the moiré lattice of molybdenum ditelluride and tungsten diselenide. |
Abstract:
A model system created by stacking a pair of monolayer semiconductors is giving physicists a simpler way to study confounding quantum behavior, from heavy fermions to exotic quantum phase transitions.
Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments
Ithaca, NY | Posted on March 24th, 2023The group’s paper, “Gate-Tunable Heavy Fermions in a Moiré Kondo Lattice,” published March 15 in Nature. The lead author is postdoctoral fellow Wenjin Zhao in the Kavli Institute at Cornell.
The project was led by Kin Fai Mak, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences, and Jie Shan, professor of applied and engineering physics in Cornell Engineering and in A&S, the paper’s co-senior authors. Both researchers are members of the Kavli Institute; they came to Cornell through the provost’s Nanoscale Science and Microsystems Engineering (NEXT Nano) initiative.
The team set out to address what is known as the Kondo effect, named after Japanese theoretical physicist Jun Kondo. About six decades ago, experimental physicists discovered that by taking a metal and substituting even a small number of atoms with magnetic impurities, they could scatter the material’s conduction electrons and radically alter its resistivity.
That phenomenon puzzled physicists, but Kondo explained it with a model that showed how conduction electrons can “screen” the magnetic impurities, such that the electron spin pairs with the spin of a magnetic impurity in opposite directions, forming a singlet.
While the Kondo impurity problem is now well understood, the Kondo lattice problem – one with a regular lattice of magnetic moments instead of random magnetic impurities – is much more complicated and continues to stump physicists. Experimental studies of the Kondo lattice problem usually involve intermetallic compounds of rare earth elements, but these materials have their own limitations.
“When you move all the way down to the bottom of the Periodic Table, you end up with something like 70 electrons in an atom,” Mak said. “The electronic structure of the material becomes so complicated. It is very difficult to describe what’s going on even without Kondo interactions.”
The researchers simulated the Kondo lattice by stacking ultrathin monolayers of two semiconductors: molybdenum ditelluride, tuned to a Mott insulating state, and tungsten diselenide, which was doped with itinerant conduction electrons. These materials are much simpler than bulky intermetallic compounds, and they are stacked with a clever twist. By rotating the layers at a 180-degree angle, their overlap results in a moiré lattice pattern that traps individual electrons in tiny slots, similar to eggs in an egg carton.
This configuration avoids the complication of dozens of electrons jumbling together in the rare earth elements. And instead of requiring chemistry to prepare the regular array of magnetic moments in the intermetallic compounds, the simplified Kondo lattice only needs a battery. When a voltage is applied just right, the material is ordered into forming a lattice of spins, and when one dials to a different voltage, the spins are quenched, producing a continuously tunable system.
“Everything becomes much simpler and much more controllable,” Mak said.
The researchers were able to continuously tune the electron mass and density of the spins, which cannot be done in a conventional material, and in the process they observed that the electrons dressed with the spin lattice can become 10 to 20 times heavier than the “bare” electrons, depending on the voltage applied.
The tunability can also induce quantum phase transitions whereby heavy electrons turn into light electrons with, in between, the possible emergence of a “strange” metal phase, in which electrical resistance increases linearly with temperature. The realization of this type of transition could be particularly useful for understanding the high-temperature superconducting phenomenology in copper oxides.
“Our results could provide a laboratory benchmark for theorists,” Mak said. “In condensed matter physics, theorists are trying to deal with the complicated problem of a trillion interacting electrons. It would be great if they don’t have to worry about other complications, such as chemistry and material science, in real materials. So they often study these materials with a ‘spherical cow’ Kondo lattice model. In the real world you cannot create a spherical cow, but in our material now we’ve created one for the Kondo lattice.”
Co-authors include doctoral students Bowen Shen and Zui Tao; postdoctoral researchers Kaifei Kang and Zhongdong Han; and researchers from the National Institute for Materials Science in Tsukuba, Japan.
The research was primarily supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the National Science Foundation, the U.S. Department of Energy and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Becka Bowyer
Cornell University
Office: 607-220-4185
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Quantum Physics
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Military
![]() Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
Quantum engineers ‘squeeze’ laser frequency combs to make more sensitive gas sensors January 17th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Quantum nanoscience
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








