Home > Press > Dual-site collaboration boosts electrochemical nitrogen reduction on Ru-S-C single-atom catalyst
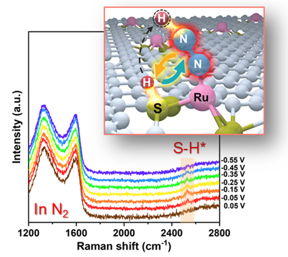 |
| Using in situ Raman spectroscopy and dynamic kinetic effect, the researchers have experimentally confirmed the positive effect of the Ru/S dual-site mechanism on eNRR over a model Ru-S-C single-atom catalyst. CREDIT Chinese Journal of Catalysis |
Abstract:
Ammonia (NH3) is a substantial important fertilizer and chemical for human society, however, its production by the traditional Haber-Bosch process consumes substantial fossil fuel energy and produces massive carbon dioxide emissions. Powered by renewable energy, electrocatalytic reduction of nitrogen (N2) to NH3 under eco-friendly and mild conditions provides a highly attractive solution to carbon neutrality. Despite recent significant progress, electrocatalytic nitrogen reduction reaction (eNRR) still suffers from limited selectivity and activity. This is due to the super-stability of N≡N triple bond. Theoretical and experimental efforts have demonstrated that the electrocatalysts always face a significant challenge to effectively activate N2 and accomplish the first protonation of N2 to form NNH* in the rate-determining step (RDS).
Dual-site collaboration boosts electrochemical nitrogen reduction on Ru-S-C single-atom catalyst
Dalian, China | Posted on January 6th, 2023One strategy to break the above limitation of eNRR is to involve multi-reaction sites in catalytic reactions, just like the catalytically active sites in talented metalloenzymes. For instance, in Fe nitrogenase, the S atom adjacent to the Fe centre functions as a co-catalytic site to bind protons (H*), which electrostatically activates the N2 molecule adsorbed by the Fe centre to the optimum state and provides H* for the hydrogenation of N2. Such a close collaboration between the metal centre and its coordination atoms enables the nitrogenase to achieve ultrahigh activity and selectivity. Therefore, one can expect that the synergetic work of multiple catalytic sites on the catalyst surface can significantly enhance the activity and selectivity of eNRR.
Recently, a research team led by Prof. Tao Ling from Tianjin University, China, proposed to realize a synergetic work of multi-reaction sites to overcome the limitation of sustainable NH3 production. Herein, using ruthenium-sulfur-carbon (Ru-S-C) catalyst as a prototype, the researchers show that the Ru/S dual-site cooperates to catalyse eNRR at ambient conditions. With the combination of theoretical calculations, in situ Raman spectroscopy, and experimental observation, the researchers demonstrate that such Ru/S dual-site cooperation greatly facilitates the activation and first protonation of N2 in the rate-determining step of eNRR. As a result, Ru-S-C catalyst exhibits significantly enhanced eNRR performance compared with the routine Ru-N-C catalyst via a single-site catalytic mechanism. It can be anticipated that the specifically designed dual-site collaborative catalytic mechanism will open up a new way to offer new opportunities for advancing sustainable NH3 production.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Fan He
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
Office: 86-411-843-79240
Copyright © Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Chemistry
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








