Home > Press > Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling
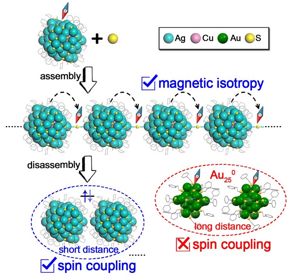 |
| The magnetism performances of Ag77Cu22 nanoclusters after assembly and disassembly (The inset in red circle presents the absence of spin coupling in Au250 due to the long interparticle distance) CREDIT XIA Nan |
Abstract:
In a recent paper published in Nature Communications, a team led by Prof. WU Zhikun from the Institute of Solid State Physics, Hefei Institutes of Physical Science (HFIPS) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), collaborated with Prof. ZENG Zhi group from the same institute and Prof. ZHAO Jijun group from Dalian University of Technology, discovered the spin transfer and spin coupling through the linear assembly of Ag-Cu alloy nanoclusters with sulfur.
Linearly assembled Ag-Cu nanoclusters: Spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling
Hefei, China | Posted on November 4th, 2022The assembly of metal nanoparticles not only enriches their properties, but also helps to understand the structure-property relationships and the interactions between nanoparticles. However, due to the multi-distribution of metal nanocrystals, it is difficult to obtain atomically precise assembly structures; The recently emerging nanoclusters (ultrasmall nanoparticles)provide ideal building blocks for precise assembly due to their well-defined compositions and structures, however, few studies on atomically precise metal nanocluster (larger than 1 nm) assembly have been reported owing to the difficulty of synthesis and characterization.
In this study, the team prepared a linear assembly structure formed by linking two Ag77Cu22 clusters with one sulfur ion using a simultaneous synthesis and assembly strategy. The sulfur ions can be produced by the cleavage of carbon-sulfur and sulfur-hydrogen bonds of the thiols during the synthesis of the clusters, leading to the immediate link with clusters to form the assemblies.
Further studies showed that the magnetic moment in this linear assembled structure was transferred from the cluster to the sulfur, forming paramagnetic sulfur radicals, which exhibited magnetic isotropy due to the small spin-orbit coupling constants of sulfur and the absence of magnetic moment interaction between distant sulfur radicals. When the linear structures were disassembled in solution, the magnetic moment transferred back to the clusters, and subsequently spin coupling occurred. Notably, such spin coupling had not been reported in the magnetic Au250 clusters, which was interpreted by the interparticle distance dependent spin coupling. When the ligands were flexible and their lengths were short, the clusters could approach each other and the spin coupling occured within a certain distance. Otherwise it was difficult for the clusters to come close for coupling.
This work successfully achieved the linear assembly of the metal nanoclusters larger than 1 nm by using the adequate assembly strategy. It discovered and explained the spin transfer and distance-dependent spin coupling, which would have important implications for the future study of nanocluster magnetism and development of novel functional materials.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Weiwei Zhao
Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
Office: 86-551-655-91206
Copyright © Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








