Home > Press > Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes
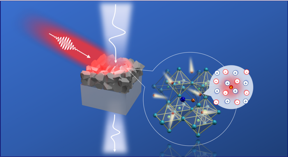 |
| The photoexcited charge carrier is “dressed” by the local lattice distortion, which is revealed by ultrafast conductivity measurements using terahertz transient. CREDIT by Zuanming Jin, Yan Peng, Yuqing Fang, Zhijiang Ye, Zhiyuan Fan, Zhilin Liu, Xichang Bao, Heng Gao, Wei Ren, Jing Wu, Guohong Ma, Qianli Chen, Chao Zhang, Alexey V. Balakin, Alexander P. Shkurinov, Yiming Zhu, Songlin Zhuang |
Abstract:
Organic-inorganic hybrid metal halide perovskites (MHPs) have attracted tremendous attention for optoelectronic applications. For example, cost-effective solar cells, solid-state lighting, memristors, and ultrafast spin switches in spintronics have recently been designed using MHPs. Despite the promise of the material, many questions remain regarding the nature and mobility of charge carriers in MHPs, which require further understanding.
Photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes
Changchun, China | Posted on July 8th, 2022Researchers from the University of shanghai for science and technology, in collaboration with Qingdao institute of bioenergy and bioprocess technology, Shanghai University, Shanghai institute of technical physics, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, and Lomonosov Moscow State University, now report photoinduced large polaron transport and dynamics in organic-inorganic hybrid lead halide perovskite with terahertz probes.
The researchers experimentally identify the photocarriers-optical phonon coupling in CH3NH3PbI3 (MAPbI3) polycrystalline grains, by using optical-pump and terahertz-electromagnetic probe spectroscopy. The photoinduced charge carrier, together with the surrounding lattice distortion over several lattice constants, forms a quasi-particle - a polaron. Using the Drude-Smith-Lorentz model along with the Frӧhlich-type electron-phonon coupling, the researchers determine the effective mass and scattering parameters of photogenerated polaronic carriers. According to the polaron mass enhancement, the polycrystalline nature of the material, and the presence of defects, the large polaron mobility is calculated on the order of ~80 cm2V−1s−1.
Furthermore, the researchers reveal that the formation of large polarons in MAPbI3 protects the charge carriers from scattering with polycrystalline grain boundaries or defects and explains the long lifetime of photoconductivity. The findings provide insights into the polaronic nature of charge carriers in MAPbI3 materials, which is relevant for both fundamental researches and device applications. The results are published in the journal Light: Science & Applications.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Media Contact
Yaobiao Li
Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
Office: 86-431-861-76851
Expert Contact
Yan Peng
University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, China
Copyright © Light Publishing Center, Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics And Physics, CAS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Perovskites
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
Memristors
![]() Artificial neurons go quantum with photonic circuits: Quantum memristor as missing link between artificial intelligence and quantum computing March 25th, 2022
Artificial neurons go quantum with photonic circuits: Quantum memristor as missing link between artificial intelligence and quantum computing March 25th, 2022
![]() New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
New brain-like computing device simulates human learning: Researchers conditioned device to learn by association, like Pavlov's dog April 30th, 2021
![]() New insights into memristive devices by combining incipient ferroelectrics and graphene November 27th, 2020
New insights into memristive devices by combining incipient ferroelectrics and graphene November 27th, 2020
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Spintronics
![]() Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Quantum materials: Electron spin measured for the first time June 9th, 2023
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








