Home > Press > Research shows old newspapers can be used to grow carbon nanotubes: Newspapers provide a green, economical way to produce carbon nanotubes
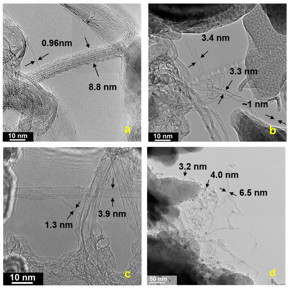 |
| TEM images of raw carbon soot grown on kaolin sized paper showing (a) roped single-walled carbon nanotubes (SWCNTs) helically wrapped by a SWCNT, and large SWCNTs, (b) collapsed, (c) folded, and (d) twisted nanotubes. Scale bar = 10 nm (a-c) and 50 nm (d). CREDIT Rice University |
Abstract:
A research collaboration between Rice University and the Energy Safety Research Institute (ESRI) at Swansea University has found that old newspapers can be used as a low cost, eco-friendly material on which to grow single walled carbon nanotubes on a large scale.
Research shows old newspapers can be used to grow carbon nanotubes: Newspapers provide a green, economical way to produce carbon nanotubes
Swansea, UK | Posted on November 22nd, 2019Carbon nanotubes are tiny molecules with incredible physical properties that can be used in a huge range of things, such as conductive films for touchscreen displays, flexible electronics, fabrics that create energy and antennas for 5G networks.
The new study, published in the MDPI Journal C , details the research experiments carried out in producing carbon nanotubes which could have the potential to solve some of the problems associated with their large scale production such as:-
The high cost of preparing a suitable surface for chemical growth.
The difficulties in scaling up the process, as only single surface growth processes have been previously available.
The research team discovered that the large surface area of newspapers provided an unlikely but ideal way to chemically grow carbon nanotubes.
Lead researcher Bruce Brinson said: "Newspapers have the benefit of being used in a roll-to-roll process in a stacked form making it an ideal candidate as a low-cost stackable 2D surface to grow carbon nanotubes."
However, not all newspaper is equally good - only newspaper produced with sizing made from kaolin, which is china clay, resulted in carbon nanotube growth.
Co-author Varun Shenoy Gangoli said: "Many substances including talc, calcium carbonate, and titanium dioxide can be used in sizing in papers which act as a filler to help with their levels of absorption and wear. However it was our observation that kaolin sizing, and not calcium carbonate sizing, showed us how the growth catalyst, which in our case was iron, is affected by the chemical nature of the substrate."
ESRI Director Andrew Barron, also a professor at Rice University in the USA, said: "While there have been previous research that shows that graphene, carbon nanotubes and carbon dots can be been synthesised on a variety of materials, such as food waste, vegetation waste, animal, bird or insect waste and chemically grown on natural materials, to date, this research has been limited.
"With our new research, we have found a continuous flow system that dramatically reduces the cost of both substrate and post synthesis process which could impact on the future mass manufacture of single walled carbon nanotubes."
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Delyth Purchase
@swanseauni
Copyright © Swansea University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








