Home > Press > Tiny, biocompatible laser could function inside living tissues: Nanolaser has potential to treat neurological disorders or sense disease biomarkers
 |
Abstract:
•Nanolaser is smaller, more stable and driven at much lower powers than existing small lasers
•Made from intrinsically biocompatible glass, it can absorb shorter and longer wavelengths of light
•Researchers developed laser by upconverting low-energy photons to visible light
Tiny, biocompatible laser could function inside living tissues: Nanolaser has potential to treat neurological disorders or sense disease biomarkers
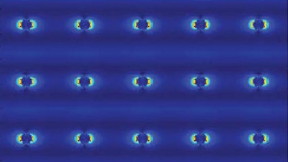
Evanston, IL | Posted on September 23rd, 2019Researchers have developed a tiny nanolaser that can function inside of living tissues without harming them.
Just 50 to 150 nanometers thick, the laser is about 1/1,000th the thickness of a single human hair. At this size, the laser can fit and function inside living tissues, with the potential to sense disease biomarkers or perhaps treat deep-brain neurological disorders, such as epilepsy.
Developed by researchers at Northwestern and Columbia Universities, the nanolaser shows specific promise for imaging in living tissues. Not only is it made mostly of glass, which is intrinsically biocompatible, the laser can also be excited with longer wavelengths of light and emit at shorter wavelengths.
“Longer wavelengths of light are needed for bioimaging because they can penetrate farther into tissues than visible wavelength photons,” said Northwestern’s Teri Odom, who co-led the research. “But shorter wavelengths of light are often desirable at those same deep areas. We have designed an optically clean system that can effectively deliver visible laser light at penetration depths accessible to longer wavelengths.”
The nanolaser also can operate in extremely confined spaces, including quantum circuits and microprocessors for ultra-fast and low-power electronics.
The paper was published today (Sept. 23) in the journal Nature Materials. Odom co-led the work with P. James Schuck at Columbia University’s School of Engineering.
While many applications require increasingly small lasers, researchers continually run into the same roadblock: Nanolasers tend to be much less efficient than their macroscopic counterparts. And these lasers typically need shorter wavelengths, such as ultraviolet light, to power them.
“This is bad because the unconventional environments in which people want to use small lasers are highly susceptible to damage from UV light and the excess heat generated by inefficient operation,” said Schuck, an associate professor of mechanical engineering.
Odom, Schuck and their teams were able to achieve a nanolaser platform that solves these issues by using photon upconversion. In upconversion, low-energy photons are absorbed and converted into one photon with higher energy. In this project, the team started with low-energy, “bio-friendly” infrared photons and upconverted them to visible laser beams. The resulting laser can function under low powers and is vertically much smaller than the wavelength of light.
“Our nanolaser is transparent but can generate visible photons when optically pumped with light our eyes cannot see,” said Odom, the Charles E. and Emma H. Morrison Professor of Chemistry in Northwestern’s Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences. “The continuous wave, low-power characteristics will open numerous new applications, especially in biological imaging.”
“Excitingly, our tiny lasers operate at powers that are orders of magnitude smaller than observed in any existing lasers,” Schuck said.
The study, “Ultralow-threshold, continuous-wave upconverting lasing from subwavelength plasmons,” was supported by the National Science Foundation (award number DMR-1608258), the Vannevar Bush Faculty Fellowship from the U.S. Department of Defense (award number N00014-17-1-3023) and the U.S. Department of Energy (DE-AC02-05CH11231). Angel Fernandez-Bravo and Danqing Wang are the paper’s co-first authors.
Odom is a member of Northwestern’s International Institute of Nanotechnology, Chemistry of Life Processes Institute and the Robert H. Lurie Comprehensive Cancer Center of Northwestern University.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Amanda Morris at 847-467-6790 or
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








