Home > Press > Exotic spiraling electrons discovered by physicists: Rutgers-led research could lead to advances in lighting and solar cells
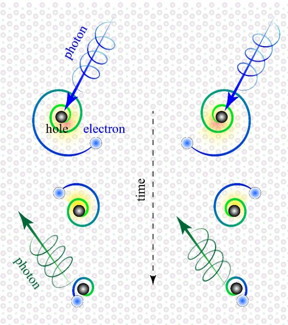 |
| The two types of 'chiral surface excitons' are on the right and left side of the image. They are generated by right- and left-handed light (photons in blue). The excitons consist of an electron (light blue) orbiting a 'hole' (black) in the same orientation as the light. The electron and hole are annihilated in less than a trillionth of a second, emitting light (photons in green) that could be harnessed for lighting, solar cells, lasers and electronic displays. CREDIT Hsiang-Hsi (Sean) Kung/Rutgers University-New Brunswick |
Abstract:
Rutgers and other physicists have discovered an exotic form of electrons that spin like planets and could lead to advances in lighting, solar cells, lasers and electronic displays.
Exotic spiraling electrons discovered by physicists: Rutgers-led research could lead to advances in lighting and solar cells
New Brunswick, NJ | Posted on February 18th, 2019It's called a "chiral surface exciton," and it consists of particles and anti-particles bound together and swirling around each other on the surface of solids, according to a study in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Chiral refers to entities, like your right and left hands, that match but are asymmetrical and can't be superimposed on their mirror image.
Excitons form when intense light shines on solids, kicking negatively charged electrons out of their spots and leaving behind positively charged "holes," according to lead author Hsiang-Hsi (Sean) Kung, a graduate student in Physics Professor Girsh Blumberg's Rutgers Laser Spectroscopy Lab at Rutgers University-New Brunswick.
The electrons and holes resemble rapidly spinning tops. The electrons eventually "spiral" towards the holes, annihilating each other in less than a trillionth of a second while emitting a kind of light called "photoluminescence." This finding has applications for devices such as solar cells, lasers and TV and other displays.
The scientists discovered chiral excitons on the surface of a crystal known as bismuth selenide, which could be mass-produced and used in coatings and other materials in electronics at room temperature.
"Bismuth selenide is a fascinating compound that belongs to a family of quantum materials called 'topological insulators,'" said senior author Blumberg, a professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy in the School of Arts and Sciences. "They have several channels on the surface that are highly efficient in conducting electricity."
The dynamics of chiral excitons are not yet clear and the scientists want to use ultra-fast imaging to further study them. Chiral surface excitons may be found on other materials as well.
###
Rutgers co-authors include doctoral students Xueyun Wang and Alexander Lee, and Board of Governors Professor Sang-Wook Cheong in Rutgers Center for Emergent Materials, who developed the ultra-pure crystals for this study. Professor Dmitrii Maslov and graduate student Adamya Goyal at the University of Florida and principal investigator Alexander Kemper at North Carolina State University contributed to theory development and the interpretation of results.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Todd Bates
848-932-0550
Copyright © Rutgers University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








