Home > Press > Optimization of alloy materials: Diffusion processes in nano particles decoded
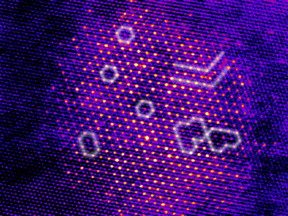 |
| Electron microscopic image of an aluminium nano-precipitate with atom-sized diffusion channels CREDIT © TU Graz / FELMI |
Abstract:
Aluminium alloys have unique material properties and are indispensable materials in aircraft manufacturing and space technology. With the help of high-resolution electron tomography, researchers at TU Graz have for the first time been able to decode mechanisms crucial for understanding these properties. The research results have recently been published in Nature Materials.
Optimization of alloy materials: Diffusion processes in nano particles decoded
Graz, Austria | Posted on November 13th, 2018Nano structures responsible for material quality
Alloy elements such as scandium and zircon are added to the aluminium matrix to improve the strength, corrosion resistance and weldability of aluminium alloys. After further treatment, tiny roundish particles only a few nanometres in size, so-called nano-precipitates, are formed. Their form, atomic structure and the 'struggle' of the scandium and zircon atoms for the 'best place' in the crystal lattice are decisive for the properties and usability of the material.
Researchers at TU Graz analysed these structures with the help of the Austrian Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope (ASTEM) at the Graz Centre for Electron Microscopy (ZFE). The device can produce high-resolution element mappings of three-dimensional structures. 'The thus arrived at tomographic analysis provided an image which, surprisingly, could not be interpreted according to the previous level of knowledge,' said Gerald Kothleitner, head of the working group for analytic transmission electron microscopy at the TU Graz's Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis. 'We detected anomalies in the generated core-shell structures. On the one hand, we found higher quantities of aluminium in the nano-precipitates then we had presumed. On the other hand, we discovered a zircon-enriched core as well as border zones between the core and shell with an almost perfect composition and crystal structure.'
Quantum mechanics and Monte Carlo methods provide answers
To track down this phenomenon of self-organisation, researchers from the Institute of Electron Microscopy and Nanoanalysis (FELMI) and the Institute of Materials Science, Joining and Forming (IMAT) fell back on quantum mechanical calculations and simulations. It was found that the system separates itself and forms atomically narrow channels in which the foreign atoms can diffuse. Atoms encountering each other block these channels and stabilise the system. Doctoral student Angelina Orthacker, whose thesis was funded by the Austrian Cooperative Research (ACR), gives a graphic explanation of the movement of the atoms: 'The diffusion process can be compared with the formation of an emergency corridor in an urban area with heavy traffic. The traffic manages to organise itself in a split second to enable the free flow of emergency vehicles. But it only takes a few individual vehicles to block the emergency corridor thus stopping it from working.' And this is exactly the same behaviour in the interior of aluminium alloys. 'Emergency corridors' promote the material transport of scandium and zircon atoms and even slight disturbances stop this transport reaction. The research team presumes that the new findings about these diffusion processes also play a role in other multi-component alloys. Their properties can now be adjusted even more.
###
This research area is anchored in the Field of Expertise "Advanced Materials Science", one of five research foci of TU Graz. Participating researchers are members of NAWI Graz - Natural Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Gerald KOTHLEITNER
43-316-873-8336
Copyright © Graz University of Technology
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Aerospace/Space
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








