Home > Press > Ultrasensitive toxic gas detector
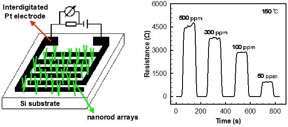 |
| A schematic illustration of the gas sensor device based on the hybrid nanorod arrays. The real time resistance versus time of the vertically aligned WO3-CuO core-shell nanorod arrays-based gas sensor to varied concentrations of NH3 decreasing from 500 ppm to 50 ppm at 150 ?. The resistance of the WO3-CuO hybrid increases upon exposure to NH3, consistent with p-type semiconductor behavior. The response of the hybrid sample increasing with increasing NH3 concentration at 150. The response and recovery times range from 10 to 15 s for all NH3 concentrations. CREDIT Author |
Abstract:
In a paper published in NANO, researchers from the School of Microelectronics in Tianjin University have discovered a two-step sputtering and subsequent annealing treatment method to prepare vertically aligned WO3-CuO core-shell nanorod arrays which can detect toxic NH3 gas.
Ultrasensitive toxic gas detector
Singapore | Posted on October 31st, 2018Over the years, WO3 has received considerable attention among the numerous transition metal oxides as a wide band-gap n-type semiconductor in various gas detection, such as NOx, H2S, H2, and NH3. CuO has the unique property of being intrinsically p-type. In the last decade, p-n heterojunction sensors composed of an n-type metal oxide and CuO were reported to have a good sensitivity to reducing gases owing to the interface between n-metal oxide and CuO. Much effort has been focused on the WO3-based nanocomposites, since the synergetic enhancement and heterojunction effects attributes to the enhanced gas sensing properties. However, gas sensors based on 1D WO3-CuO composite structures are limited. Additionally, the template or catalyst was usually necessary to synthesize WO3-based nanorod arrays, including using chemical vapor deposition, electrochemical anodization and hydrothermal approaches.
Among toxic gases causing adverse impact on living organisms, NH3 is one of the most hazardous substances. It is necessary to build up ultrasensitive NH3 gas sensors with short response and recovery time. Metal oxides have been widely used in gas sensor applications. In order to obtain great sensing performances of metal oxide sensors, 1D metal oxide nanostructures and 1D heterojunction composite nanostructures have been investigated due to their large surface area, size-dependent properties, and the nano-heterojunction effects. Vertically aligned ordered 1D arrays effectively avoid the dense stacking of rod monomers, especially, resulting in novel physicochemical characteristics, such as higher gas response and shorter gas recovery.
Here, vertically aligned WO3-CuO core-shell nanorod arrays are synthesized using a non-catalytic two-step annealing process of sputtered metal film on silicon wafer. The growth mechanism of the vertically aligned nanorod arrays are discussed. The NH3 sensing behaviors of the WO3-CuO core-shell arrays at different temperatures are reported. A possible NH3 sensing mechanism for the hybrid is proposed.
###
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 61271070, 61274047) and Tianjin Key Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology, China (Grant No. 11JCZDJC15300).
The corresponding author of this study is Wenjun Yan.
For more insight into the research described, readers are invited to access the paper on NANO.
####
About World Scientific
World Scientific Publishing is a leading independent publisher of books and journals for the scholarly, research, professional and educational communities. The company publishes about 600 books annually and about 135 journals in various fields. World Scientific collaborates with prestigious organizations like the Nobel Foundation and US National Academies Press to bring high quality academic and professional content to researchers and academics worldwide. To find out more about World Scientific, please visit http://www.worldscientific.com.
NANO is an international peer-reviewed monthly journal for nanoscience and nanotechnology that presents forefront fundamental research and new emerging topics. It features timely scientific reports of new results and technical breakthroughs and publishes interesting review articles about recent hot issues.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tay Yu Shan
Copyright © World Scientific
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








