Home > Press > Genetically engineered virus spins gold into beads: The discovery could make production of some electronic components cheaper, easier, and faster
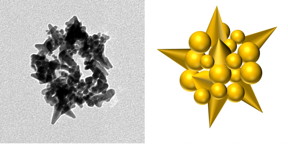 |
| Electron microscope image of M13 spheroid-templated spiky gold nanobead with corresponding graphical illustration. CREDIT Haberer Lab, UC Riverside |
Abstract:
The race is on to find manufacturing techniques capable of arranging molecular and nanoscale objects with precision.
Engineers at the University of California, Riverside, have altered a virus to arrange gold atoms into spheroids measuring a few nanometers in diameter. The finding could make production of some electronic components cheaper, easier, and faster.
Genetically engineered virus spins gold into beads: The discovery could make production of some electronic components cheaper, easier, and faster
Riverside, CA | Posted on August 25th, 2018"Nature has been assembling complex, highly organized nanostructures for millennia with precision and specificity far superior to the most advanced technological approaches," said Elaine Haberer, a professor of electrical and computer engineering in UCR's Marlan and Rosemary Bourns College of Engineering and senior author of the paper describing the breakthrough. "By understanding and harnessing these capabilities, this extraordinary nanoscale precision can be used to tailor and build highly advanced materials with previously unattainable performance."
Viruses exist in a multitude of shapes and contain a wide range of receptors that bind to molecules. Genetically modifying the receptors to bind to ions of metals used in electronics causes these ions to "stick" to the virus, creating an object of the same size and shape. This procedure has been used to produce nanostructures used in battery electrodes, supercapacitors, sensors, biomedical tools, photocatalytic materials, and photovoltaics.
The virus' natural shape has limited the range of possible metal shapes. Most viruses can change volume under different scenarios, but resist the dramatic alterations to their basic architecture that would permit other forms.
The M13 bacteriophage, however, is more flexible. Bacteriophages are a type of virus that infects bacteria, in this case, gram-negative bacteria, such as Escherichia coli, which is ubiquitous in the digestive tracts of humans and animals. M13 bacteriophages genetically modified to bind with gold are usually used to form long, golden nanowires.
Studies of the infection process of the M13 bacteriophage have shown the virus can be converted to a spheroid upon interaction with water and chloroform. Yet, until now, the M13 spheroid has been completely unexplored as a nanomaterial template.
Haberer's group added a gold ion solution to M13 spheroids, creating gold nanobeads that are spiky and hollow.
"The novelty of our work lies in the optimization and demonstration of a viral template, which overcomes the geometric constraints associated with most other viruses," Haberer said. "We used a simple conversion process to make the M13 virus synthesize inorganic spherical nanoshells tens of nanometers in diameter, as well as nanowires nearly 1 micron in length."
The researchers are using the gold nanobeads to remove pollutants from wastewater through enhanced photocatalytic behavior.
The work enhances the utility of the M13 bacteriophage as a scaffold for nanomaterial synthesis. The researchers believe the M13 bacteriophage template transformation scheme described in the paper can be extended to related bacteriophages.
###
The project is supported by award number N00014-14-1-0799 from the U.S. Office of Naval Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Holly Ober
951-827-5893
Copyright © University of California - Riverside
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








