Home > Press > Researchers present new strategy for extending ductility in a single-phase alloy
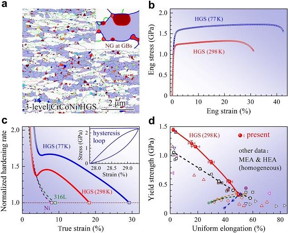 |
| A. Multilevel heterogeneous structure of single-phase CrCoNi medium entropy alloy after tensile test: Micrometer-sized grains (white), submicron grains (blue), nanograins (colored). Nanograin forms at grain boundaries of submicron grains. B. Tensile properties. C. Normalized work hardening rate. D. Combination of yield strength and uniform elongation. CREDIT WU Xiaolei |
Abstract:
Simultaneous high strength and large ductility are always desirable for metallic materials. However, while the strength of metals and alloys can be easily increased by 5-15 times through simple plastic deformation or grain refinement down to the nano-scale, the gain in strength is usually accompanied by a drastic loss of uniform ductility. Ductility depends strongly on the work hardening ability, which becomes weak in materials with high strength, especially in a single-phase material.
Researchers present new strategy for extending ductility in a single-phase alloy
Beijing, China | Posted on June 28th, 2018Publishing online in PNAS, the research group of Prof. WU Xiaolei at the State Key Laboratory of Nonlinear Mechanics, Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, in collaboration with Prof. En Ma at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, USA, have demonstrated a strategy for exploiting a dynamically reinforced multilevel heterogeneous grain structure (HGS).
They demonstrated the behavior of such an HGS using the face-centered-cubic CrCoNi medium-entropy alloy (MEA) as a model system.
Back stress hardening is usually not obvious in single-phase homogeneous grains. To overcome this, the scientists purposely created an unusually heterogeneous grain structure.
They took advantage of the low stacking fault energy of the MEA, which facilitates the generation of twinned nano-grains and stacking faults during tensile straining, dynamically reinforcing the heterogeneity on the fly.
For the resultant extreme HGS, back stress hardening can be made unusually strong and sustained to large tensile strains after yielding at gigapascal stress, in the absence of heterogeneities from any second phase.
Specifically, using cold rolling and recrystallization annealing, the researchers skillfully constructed an HGS with three-level grain sizes (micrometer, submicron, and nanometer), across which stress and strain partitioning occur when the HGS is plastically deformed.
Especially, new nano-grains form at grain corners due to the larger stresses there. This dynamic grain refinement, similar to the TWIP effect and the TRIP effect, contributes to the back stress hardening, which is found to be the largest in all the alloys reported so far.
This HGS achieves in a single-phase, simple-structured (FCC) alloy a strength-ductility combination that would normally require complex heterogeneities such as in multi-phase steels.
###
This research was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, and the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
WU Xiaolei
Copyright © CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES HEADQUARTERS
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








