Home > Press > Nanoparticles with pulse laser controlled antibacterial properties
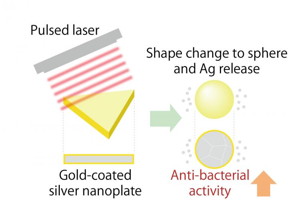 |
| When gold-coated silver nanoplates are irradiated with a pulsed laser, they change shape into a sphere and release silver ions which produces a strong antibacterial effect. CREDIT Dr. Takuro Niidome |
Abstract:
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are known to have excellent antibacterial properties and are considered by many to be a strong contender in the critical search for an answer to antibiotic-resistant bacteria. They block enzymes and can cause bacteria to have irregularly shaped membranes, producing results ranging from inhibited growth to cell death. However, a collaboration of researchers from Kumamoto University, Keio University, and Dai Nippon Toryo Co., Ltd. in Japan found that AgNPs have a propensity to conglomerate, which results in a reduction of antibacterial attributes. They solved the conglomeration problem by coating the nanoparticles with gold. Unfortunately, this also caused a reduction of the antibacterial effects since the silver was no longer exposed. This prompted the researchers to search for a method to keep the shape of the nanoparticles as well as the antibacterial properties.
Nanoparticles with pulse laser controlled antibacterial properties
Kumamoto, Japan | Posted on October 26th, 2017Pulsed laser irradiation on the gold-coated silver nanoparticles NPs) provided a solution to the problem. When NPs are irradiated with a pulse laser, the morphology of the NPs changes from a triangular plate to a spherical shape. This is due to the metals melting from the heat of the laser pulse. The researchers showed that NPs were about half triangular and half spherical before irradiation but jumped to 94% spherical after irradiation. Furthermore, the silver-to-gold ratio of the pre-irradiation NPs was around 22:1, but the post-irradiation ratio was near 4.5:1. This was interpreted by the researchers as the generation of defects in the gold-coating which allowed for some of the silver to escape as ions. This is an important aspect of the pulsed laser irradiation process since the release of silver produces the bactericidal effect.
"We have developed a method to activate the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles at will," said Professor Takuro Niidome, leader of the research group. "Our experiments have shown that, while non-irradiated gold-coated silver nanoparticles have only minor antibacterial properties, the effects are significantly increased after pulsed laser irradiation. We hope to develop this technology further as a method of managing bacteria that have developed antibacterial resistance."
The irradiated NPs were highly effective against Escherichia coli, resulting in a 0% colony survival rate. Silver NPs alone were similarly effective, but the NPs had the advantages of being activated as needed and did not tend to clump together like the silver NPs.
This research was posted online in the Royal Society of Chemistry journal Nanoscale on 11 October 2017.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
J. Sanderson
Copyright © Kumamoto University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








