Home > Press > What can be discovered at the junction of physics and chemistry
 |
| These are closed-shell paramagnetic porphyrinoids. CREDIT Rashid Valiev |
Abstract:
TSU scientist Rashid Valiev and colleagues from the universities of Helsinki and Oslo have discovered a new type of rare molecules whose properties can be controlled by changing the induction of an external magnetic field. These are paramagnetic molecules from the class porphyrins. Porphyrins are part of hemoglobin and chlorophyll and are closely related to the processes of photosynthesis and respiration in living organisms. The results of the study were published in the journal Chemical Communications of the Royal British Chemical Society.
What can be discovered at the junction of physics and chemistry
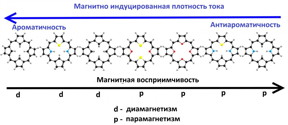
Tomsk, Russia | Posted on October 6th, 2017Open paramagnetic porphyrins with a closed electron shell are very rare molecules, because they have a specific electronic structure. Usually, molecules with such a structure are very unstable, and open porphyrins, on the contrary, are unchanged even in the air around us. This makes it possible to manipulate their physicochemical properties with an external magnetic field in various applied fields of magnetooptics and nanotechnology.
Since 2012, a group of scientists, which includes an assistant professor at TSU, has studied the aromatic nature of porphyrins and their derivatives. Aromaticity is a special property of some chemical compounds to exhibit anomalously high stability. That is an important concept in theoretical chemistry and is closely related to the problem of classifying and arranging organic molecules according to their reactivity. However, scientists define it using physics, in particular, they calculate in the molecules magnetically induced currents.
For me, it was always interesting for the physicist to connect our currents and the concept of aromaticity with the spectroscopic or physical properties of molecules,- says Rashid Valiev. - This was done in 2017 for highly antiaromatic porphyrins. Such molecules can be used in magnetooptical problems, where the control of physical properties of molecules is used by changing the induction of an external magnetic field. The fundamental significance of our result is that we explained the nature of the paramagnetism of these molecules.
Using theoretical methods of quantum chemistry, Valiev and his colleagues from the universities of Helsinki and Oslo studied the magnetic properties of seven molecules of isoflorines and carbaporphyrins, both synthesized and hypothetical. They showed that four of the seven molecules considered exhibit paramagnetism, and their spin is zero in the ground electronic state, which is an extremely rare case.
####
About National Research Tomsk State University
The Department of Optics and Spectroscopy of the Faculty of Physics and Engineering (head of the department is Victor Cherepanov), whose associate professor is Rashid Valiev, traditionally deals with the modeling of physical and chemical properties of molecules and molecular systems for various applied problems of medicine, astronomy, biology, and chemistry. The Faculty of Physics is part of the StrAU Institute of Smart Materials and Technology (SMTI).
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Tatiana Arsenyeva
Copyright © National Research Tomsk State University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








