Home > Press > Nothing -- and something -- give concrete strength, toughness: Rice University scientists show how voids, particles sap energy from cracks
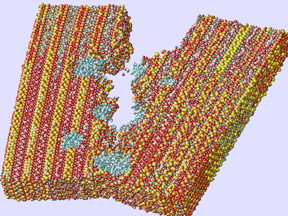 |
| Rice University researchers used computer models of concrete's inner matrix to show how tiny holes filled with portlandite (blue) impart strength and toughness by preventing the spread of cracks. Image by Ning Zhang/Rice University |
Abstract:
What does one need to strengthen or toughen concrete? A lot of nothing. Or something.
The "nothing" is in the form of microscopic voids and the "something" consists of particular particles embedded in the most common construction material on Earth. Rice University materials scientist Rouzbeh Shahsavari and postdoctoral researcher Ning Zhang analyzed more than 600 computer models of concrete's inner matrix to determine that both voids and portlandite particles are significant players in giving the material its remarkable qualities.
Nothing -- and something -- give concrete strength, toughness: Rice University scientists show how voids, particles sap energy from cracks
Houston, TX | Posted on August 8th, 2016The research appears this month in the Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids.
Shahsavari and his team set out to provide new insights and to design guidelines and strategies to make the cement hydrate -- known as calcium-silicate-hydrate (C-S-H) -- at the heart of concrete more tunable from the molecules up. They found that while concrete may appear brittle at the macroscale, it incorporates ductile fracture mechanisms at the nanoscale that help to keep it from failing.
"C-S-H is the smallest building block in concrete, and we want to understand and control it to our advantage," Shahsavari said. "Modeling how its molecules interact helps us understand its nanoscale structure, defects and fracture toughness. But this is very difficult to study through experiments alone because of the scale of the features we're looking at."
This latest in a series of studies from the Rice lab looks at how the interaction of either random air voids or random portlandite particles in C-S-H influence the mechanical qualities of strength, stiffness and toughness, especially where voids meet propagating cracks.
"Besides C-S-H, portlandite is another product of cement hydration, but it forms in lower quantities compared with C-S-H and mainly exists as sort of inclusions or isolated islands surrounded by the C-S-H matrix," Shahsavari said. "Because portlandite has different crystalline features and mechanical properties than C-S-H, its presence and distribution can significantly impact the mechanics of C-S-H."
Using molecular dynamics simulations, the researchers found that cracks tended to follow the path of least resistance and turn in the direction of either the nanovoids or portlandite particles they encountered. By deflecting or changing the geometry of a crack, the voids and particles sapped the crack of energy. Shahsavari said this likely contributes to concrete's overall toughness.
"When it comes to cement hydrate's strength and toughness -- properties that are typically exclusive in man-made materials -- random voids and portlandite particles play a key role by regulating a series of competing deformation mechanisms, such as crack growth, crack deflection, voids coalescence, internal necking, accommodation and geometry alteration of voids and particles," Shahsavari said. "Our work decoded all such complex competing mechanisms."
For C-S-H that is more amorphous than crystalline (as in tobermorite concrete), they found the addition of portlandite particles induced strong chemical reactions that increased the strength as well as the toughness of the product. They also determined that for all the variations tested, the smaller the mean diameter of both voids and particles, the stronger the material.
Since more than 30 billion tons of concrete are used each year and its manufacture contributes up to 10 percent of carbon dioxide emissions worldwide, the payoff from any small tweak is worth the effort, Shahsavari said.
"Our results provide, for the first time, new evidence of ductile fracture mechanisms in cement hydrate that are reminiscent of crystalline alloys and ductile metals," Shahsavari said. "Given that crack growth and strength are an inherent property controlled by nanoscale deformation mechanisms, our findings can impact the mechanical properties of concrete at larger scales, opening up new opportunities and strategies to turn brittle cement hydrate into a ductile material. This would impact the modern engineering of durable concrete infrastructures and potentially other complex brittle materials."
The National Science Foundation, the National Institutes of Health and an IBM Shared University Research Award in partnership with CISCO, Qlogic and Adaptive Computing supported the research.
The researchers used the NSF-supported DAVinCI supercomputer administered by Rice's Center for Research Computing and procured in a partnership with Rice's Ken Kennedy Institute.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for best quality of life and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview.
Follow Rice News and Media Relations on Twitter @RiceUNews.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jade Boyd
713-348-6778
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The DOI of the Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids paper is: 10.1016/j.jmps.2016.07.021
The DOI of the Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids paper is: 10.1016/j.jmps.2016.07.021
![]() Multiscale Materials Laboratory homepage:
Multiscale Materials Laboratory homepage:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
Construction
![]() Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
Temperature-sensing building material changes color to save energy January 27th, 2023
![]() Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
Strain-sensing smart skin ready to deploy: Nanotube-embedded coating detects threats from wear and tear in large structures July 15th, 2022
![]() A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
A sunlight-driven “self-healing” anti-corrosion coating May 27th, 2022
![]() Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
Polymer fibers with graphene nanotubes make it possible to heat hard-to-reach, complex-shaped items February 11th, 2022
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








