Home > Press > Yale researchers’ technology turns wasted heat into power
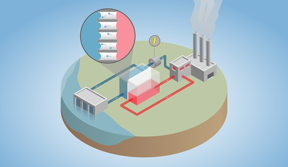 |
| The temperature difference between a waste heat source and the environment drives water across the nanobubble membrane (enlarged) and through a turbine to generate electricity.
Credit: Yale University |
Abstract:
Researchers at Yale have developed a new technology that could make energy from the low-temperature wasted heat produced by industrial sources and power plants, tapping into a widely available — and mostly unused — resource.
Yale researchers’ technology turns wasted heat into power
New Haven, CT | Posted on June 27th, 2016It is estimated that recoverable waste heat in the U.S. alone could power tens of millions of homes. Although existing technologies can reuse high-temperature heat or convert it to electricity, it is difficult to efficiently extract energy from low-temperature heat waste due to the small temperature difference between the plant’s heat discharge and the surrounding environment. Additionally, conventional systems are designed to target a specific temperature difference, so they’re less effective when there are fluctuations in the output of waste heat.
Researchers at Yale’s Department of Chemical and Environmental Engineering have developed a new technology that overcomes these challenges. The key is a “nanobubble membrane” that traps tiny air bubbles within its pores when immersed in water. Heating one side of the membrane causes water to evaporate, travel across the air gap, and condense on the opposite side of the membrane. This temperature-driven flow of water across the membrane is then directed to a turbine to generate electricity.
To prove the concept, the team built a small-scale system and demonstrated that the nanobubble membranes could produce pressurized flows of water and generate power even with heat fluctuations and temperature differences as small as 20 degrees Celsius — making it feasible for use with the wasted heat from industrial sources. The findings were published online June 27 in the journal Nature Energy.
The researchers used nanostructured membranes with a surface chemistry that helps trap the air bubbles, keeping bubbles contained within pores even when large pressures are generated. These membranes, approximately as thick as two sheets of paper, were made from highly hydrophobic (water-repelling) polymer nanofibers.
“It was critical to identify robust air-trapping membranes that facilitate pressure generation,” said Menachem Elimelech, corresponding author on the paper and the Roberto C. Goizueta Professor of Chemical and Environmental Engineering at Yale. “Without the right membrane, water would displace the air in the pores, and the process would not be feasible.”
The demonstration of the prototype convinced the researchers of the value of the technology.
“We found that the efficiency of this system can exceed that of comparable technologies,” said Anthony Straub, first author on the study and a doctoral student in chemical and environmental engineering. “The process also only uses water, so it is cost-effective and environmentally friendly.”
The researchers plan to continue work on the technology, developing improved membranes that can better trap air bubbles. They also are investigating how large-scale future systems will perform.
In addition to Elimelech and Straub, the research team included Ngai Yin Yip, a former doctoral student at Yale and current assistant professor at Columbia University; Shihong Lin, a former Yale postdoc and current assistant professor at Vanderbilt University; and Jongho Lee, a postdoc in chemical and environmental engineering at Yale.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
William Weir
203-317-9267
Copyright © Yale University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Industrial
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
Quantum interference in molecule-surface collisions February 28th, 2025
![]() Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Boron nitride nanotube fibers get real: Rice lab creates first heat-tolerant, stable fibers from wet-spinning process June 24th, 2022
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








