Home > Press > Incredible images reveal bacteria motor parts in unprecedented detail
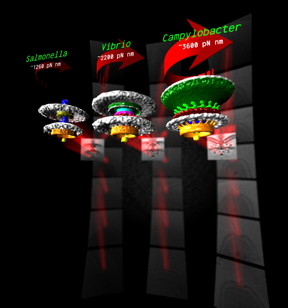 |
| These are three bacterial motors with different torque (units of torque are piconewton nanmometres, pN nm). CREDIT: Morgan Beeby/Imperial College London |
Abstract:
Many bacteria swim using flagella - long tails that are attached to tiny motors made of proteins, just tens of nanometres wide. These motors spin the flagella, which work as nanoscale propellers to drive the bacterium forward.
Incredible images reveal bacteria motor parts in unprecedented detail
London, UK | Posted on March 16th, 2016Despite motors in diverse bacteria having the same core structure, different bacteria vary widely in their swimming power. For example, Campylobacter jejuni, which causes food poisoning, can swim powerfully enough to bore through the mucus that lines the gut, an environment too thick and sticky for other bacteria to push through.
The reasons for these differences in swimming ability have remained obscure - until now. Using a recently installed high-powered electron microscope at Imperial, a team of researchers lead by Dr Morgan Beeby from the Department of Life Sciences has been able visualize these motors in unprecedented detail.
Their visualizations of these motors explains the differences in swimming ability, mathematically accounting for differences in motor power. The work is published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Bacterial flagellar motors work on a rotational mechanism, spinning their long flagellar tail to produce a helical propeller-like motion. The team found that stronger swimmers have evolved by adding extra parts to their motors, making more powerful motors that have increased turning force, or torque.
In flagellar motors, the turning force is produced by a ring of structures called stators around the motor. The team found that Campylobacter jejuni had almost twice as many stators positioned around the motor than in Salmonella, and that these structures sat in a wider ring. More stators provide increased torque, and the increased width of the ring means individual stators exert more leverage when rotating the helical propeller.
However, not all bacteria need to be so powerful and swim through such viscous environments as stomach mucus. Instead, another bacterium the team looked at, a close relative of Vibrio cholerae, the bacterium that causes cholera, has evolved a motor with only intermediate power.
"For the first time, we have been able to see and explain how these nanoscale molecular machines have evolved in bacteria to colonize new environments," said Dr Beeby. "It's a fascinating insight into the awe-inspiring diversity of life that has evolved on Earth, and also presents possible drug targets. We may be able to design drugs that specifically sabotage the flagella only in targeted bacterial species."
The team used a method called electron cryo-tomography to rapidly freeze the bacteria to -180 C. This prevents ice crystals from forming that would break the structure apart, allowing the researchers to image the flash-frozen motor from all angles and build up a 3D model.
By looking at distantly related bacteria from different branches of the evolutionary tree, the team speculate that the ability to alter torque in this way may have evolved up to two billion years ago.
"Entire branches of the bacterial family tree have evolved motors with different torques, leading to a diversity of species each geared to their own environment," said Dr Beeby. The team is now investigating how and when the evolutionary steps that altered motor torque happened.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Hayley Dunning
020-759-42412
Copyright © Imperial College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
Imaging
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








