Home > Press > Experiment records extreme quantum weirdness: An experiment in Singapore has pushed quantum weirdness close to its absolute limit
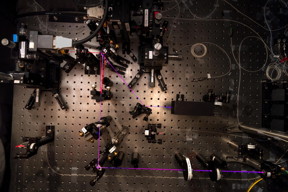 |
| This experiment at the Centre for Quantum Technologies in Singapore has made a record measurement of entanglement -- approaching the quantum limit with extreme precision.
Photo Credit: Alessandro Cerč / Centre for Quantum Technologies, National University of Singapore |
Abstract:
Researchers from the Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT) at the National University of Singapore and the University of Seville in Spain have reported the most extreme 'entanglement' between pairs of photons ever seen in the lab. The result was published 30 October 2015 in Physical Review Letters.
Experiment records extreme quantum weirdness: An experiment in Singapore has pushed quantum weirdness close to its absolute limit
Singapore | Posted on November 10th, 2015The achievement is evidence for the validity of quantum physics and will bolster confidence in schemes for quantum cryptography and quantum computing designed to exploit this phenomenon.
"For some quantum technologies to work as we intend, we need to be confident that quantum physics is complete," says Poh Hou Shun, who carried out the experiment at CQT. "Our new result increases that confidence," he says.
Local realism
Entanglement says that two particles, such as photons, can be married into a joint state. Once in such a state, either particle observed on its own appears to behave randomly. But if you measure both particles at once, you notice they are perfectly synchronized.
Albert Einstein was famously troubled by this prediction of quantum physics. He didn't like the randomness that came with just one particle. He said "God does not play dice". He didn't like the correlations that came with two particles, either. He referred to this as "spooky action at a distance".
Experiments since the 1970s have been collecting evidence that quantum predictions are correct. Recently an experiment in the Netherlands became the first to do away with all assumptions in the data-gathering.
Technically known as a 'loophole-free Bell test', the experiment leaves no wiggle room in meaning: entangled particles do behave randomly, and they synchronize without exchanging signals. (The results appeared in Nature on 21 October 2015, doi:10.1038/nature15759).
Entangled to the max
In the lab in Singapore, Poh and his colleagues also performed a Bell test. But instead of closing loopholes, their setup pushes the entanglement towards its theoretical maximum.
They make entangled photons by shining a laser through a crystal. The photons interact with the crystal in such a way that occasionally, one splits into two and the pair emerges entangled. The team control the photons with an array of lenses, mirrors and other optical elements to optimize the effect.
The researchers looked at 33.2 million optimized photon pairs. Each pair was split up and the photons measured separately, then the correlation between the results quantified.
In such a Bell test, the strength of the correlation says whether or not the photons were entangled. The measures involved are complex, but can be reduced to a simple number. Any value bigger than 2 is evidence for quantum effects at work. But there is also an upper limit.
Quantum physics predicts the correlation measure cannot get any bigger than 2sqrt(2) ~2.82843. In the experiment at CQT, they measure 2.82759 ± 0.00051 - within 0.03% of the limit. If the peak value were the top of Everest, this would be only 2.6 metres below the summit.
No extensions
The record result also rules out a proposed extension to quantum theory. Earlier this year, Alexei Grinbaum with CEA in France put forward a model in which quantum physics is just an effective description of a more fundamental theory. He calculated a new limit on the correlation measure using tools from information theory. The calculations considered how much information an observer can hold about a two-particle system, and gave a limit on the correlation measure sitting just 0.1% under the quantum limit.
"You need a very precise measurement to be able to distinguish the quantum limit, and that was our achievement," says Christian Kurtsiefer, a Principal Investigator at CQT and co-author on the paper. The team's result exceeds the Grinbaum limit by enough to rule out the model behind it.
Entanglement doesn't allow faster-than-light communication, but it can be used for secret messaging and to speed up some calculations. Checking that it's possible to reach the quantum limit for correlations is valuable for these applications: their security and reliability depends on this limit being fundamental.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jenny Hogan
Researcher contacts:
Ho Shun Poh
PhD Student, Centre for Quantum Technologies, National University of Singapore
Phone: +65 6516 6430
Christian Kurtsiefer
Principal Investigator, Centre for Quantum Technologies, National University of Singapore
Phone:+65 6516 1250
Copyright © University of Singapore
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








