Home > Press > Researchers take first steps to create biodegradable displays for electronics
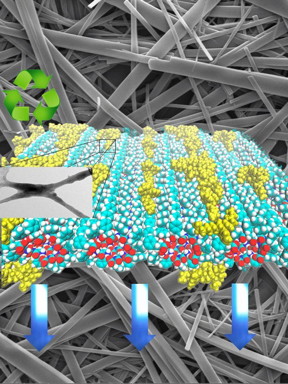 |
| The illustration shows a theoretical simulation of the distribution of the polymer on peptide nanotubes and an electron microscopy image of the nanocomposite. CREDIT: Suchi Guha, University of Missouri |
Abstract:
Americans, on average, replace their mobile phones every 22 months, junking more than 150 million phones a year in the process. When it comes to recycling and processing all of this electronic waste, the World Health Organization reports that even low exposure to the electronic elements can cause significant health risks. Now, University of Missouri researchers are on the path to creating biodegradable electronics by using organic components in screen displays. The researchers' advancements could one day help reduce electronic waste in the world's landfills.
Researchers take first steps to create biodegradable displays for electronics
Columbia, MO | Posted on October 16th, 2015"Current mobile phones and electronics are not biodegradable and create significant waste when they're disposed," said Suchismita Guha, professor in the Department of Physics and Astronomy at the MU College of Arts and Science. "This discovery creates the first biodegradable active layer in organic electronics, meaning--in principle--we can eventually achieve full biodegradability."
Guha, along with graduate student Soma Khanra, collaborated with a team from the Federal University of ABC (UFABC) in Brazil to develop organic structures that could be used to light handheld device screens. Using peptides, or proteins, researchers were able to demonstrate that these tiny structures, when combined with a blue light-emitting polymer, could successfully be used in displays.
"These peptides can self-assemble into beautiful nanostructures or nanotubes, and, for us, the main goal has been to use these nanotubes as templates for other materials," Guha said. "By combining organic semiconductors with nanomaterials, we were able to create the blue light needed for a display. However, in order to make a workable screen for your mobile phone or other displays, we'll need to show similar success with red and green light-emitting polymers."
The scientists also discovered that by using peptide nanostructures they were able to use less of the polymer. Using less to create the same blue light means that the nanocomposites achieve almost 85 percent biodegradability.
"By using peptide nanostructures, which are 100 percent biodegradable, to create the template for the active layer for the polymers, we are able to understand how electronics themselves can be more biodegradable," Guha said. "This research is the first step and the first demonstration of using such biology to improve electronics."
The study "Self-Assembled Peptide-Polyfluorene Nanocomposites for Biodegradable Organic Electronics" recently was published as the inside cover article in Advanced Materials Interfaces. The work was supported by the National Science Foundation (Grant IIA-1339011) and CNPq (400239/2014-0). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funding agencies.
Tommi White, assistant research professor of biochemistry, and Thomas Lam, both with the Microscopy Core Research Facility at MU, contributed to the study. Other collaborators include Wendel A. Alves and Thiago Cipriano, professors of supramolecular chemistry at UFABC; Eudes E. Fileti, a professor of physics at the Federal University of São Paulo, Brazil.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jeff Sossamon
573-882-3346
Copyright © University of Missouri-Columbia
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Editor's Note: For more on the story, please see:
Editor's Note: For more on the story, please see:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Environment
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








