Home > Press > Nano-trapped molecules are potential path to quantum devices
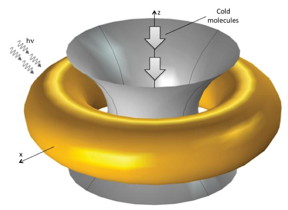 |
| With a nano-ring-based toroidal trap, cold polar molecules near the gray shaded surface approaching the central region may be trapped within a nanometer scale volume. CREDIT: ORNL |
Abstract:
Single atoms or molecules imprisoned by laser light in a doughnut-shaped metal cage could unlock the key to advanced storage devices, computers and high-resolution instruments.
Nano-trapped molecules are potential path to quantum devices
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on September 18th, 2015In a paper published in Physical Review A, a team composed of Ali Passian of the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Marouane Salhi and George Siopsis of the University of Tennessee describes conceptually how physicists may be able to exploit a molecule's energy to advance a number of fields.
"A single molecule has many degrees of freedom, or ways of expressing its energy and dynamics, including vibrations, rotations and translations," Passian said. "For years, physicists have searched for ways to take advantage of these molecular states, including how they could be used in high-precision instruments or as an information storage device for applications such as quantum computing."
Catching a molecule with minimal disturbance is not an easy task, considering its size - about a billionth of a meter - but this paper proposes a method that may overcome that obstacle.
When interacting with laser light, the ring toroidal nanostructure - sort of like a doughnut shrunk a million times -- can trap the slower molecules at its center. This happens as the nano-trap, which can be made of gold using conventional nanofabrication techniques, creates a highly localized force field surrounding the molecules. The team envisions using scanning probe microscopy techniques to access individual nano-traps that would be part of an array.
"The scanning probe microscope offers a great deal of maneuverability at the nanoscale in terms of measuring extremely small forces," Passian said. "This is a capability that will undoubtedly be useful for future trapping experiments.
"Once trapped, we can interrogate the molecules for their spectroscopic and electromagnetic properties and study them in isolation without disturbance from the neighboring molecules."
While previous demonstrations of trapping molecules have relied on large systems to confine charged particles such as single ions, this new concept goes in the opposite direction, at the nanoscale. Next, Passian, Siopsis and Salhi plan to build actual nanotraps and conduct experiments to determine the feasibility of fabricating a large number of traps on a single chip.
"If successful, these experiments could help enable information storage and processing devices that greatly exceed what we have today, thus bringing us closer to the realization of quantum computers," Passian said.
Salhi envisions a similar future, saying, "These advances are unveiling the beauty of the optical response for many complex geometries and opening the door to handcrafting the electromagnetic environment. We envision applications not only for trapping but also in designing new optically active devices."
####
About DOE/Oak Ridge National Laboratory
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the DOE's Office of Science. The Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov/.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ron Walli
865-576-0226
Copyright © DOE/Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() The paper, titled "Toroidal nano-traps for cold polar molecules," is available at:
The paper, titled "Toroidal nano-traps for cold polar molecules," is available at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








