Home > Press > A little light interaction leaves quantum physicists beaming
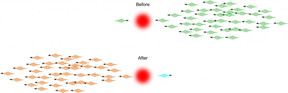 |
| This is an artist's rendition of what occurs when one photon goes through a carefully prepared atomic medium at the same time as a pulse including many photons. Change in the colors, represents nonlinear phase shifts picked up by each pulse that is proportional to the number of photons in the other pulse. A measurable nonlinear phase shift caused by a single photon on a pulse with many photons can enable deterministic two-qubit gates, an important missing part of the optical quantum information processing hardware. CREDIT: Amir Feizpour |
Abstract:
A team of physicists at the University of Toronto (U of T) have taken a step toward making the essential building block of quantum computers out of pure light. Their advance, described in a paper published this week in Nature Physics, has to do with a specific part of computer circuitry known as a "logic gate."
A little light interaction leaves quantum physicists beaming
Toronto, Canada | Posted on August 25th, 2015Logic gates perform operations on input data to create new outputs. In classical computers, logic gates take the form of diodes or transistors. But quantum computer components are made from individual atoms and subatomic particles. Information processing happens when the particles interact with one another according to the strange laws of quantum physics.
Light particles - known as "photons" - have many advantages in quantum computing, but it is notoriously difficult to get them to interact with one another in useful ways. This experiment demonstrates how to create such interactions.
"We've seen the effect of a single particle of light on another optical beam," said Canadian Institute for Advanced Research (CIFAR) Senior Fellow Aephraim Steinberg, one of the paper's authors and a researcher at U of T's Centre for Quantum Information & Quantum Computing. "Normally light beams pass through each other with no effect at all. To build technologies like optical quantum computers, you want your beams to talk to one another. That's never been done before using a single photon."
The interaction was a two-step process. The researchers shot a single photon at rubidium atoms that they had cooled to a millionth of a degree above absolute zero. The photons became "entangled" with the atoms, which affected the way the rubidium interacted with a separate optical beam. The photon changes the atoms' refractive index, which caused a tiny but measurable "phase shift" in the beam.
This process could be used as an all-optical quantum logic gate, allowing for inputs, information-processing and outputs.
"Quantum logic gates are the most obvious application of this advance," said Steinberg. "But being able to see these interactions is the starting page of an entirely new field of optics. Most of what light does is so well understood that you wouldn't think of it as a field of modern research. But two big exceptions are, "What happens when you deal with light one particle at a time?' and "What happens when there are media like our cold atoms that allow different light beams to interact with each other?'"
Both questions have been studied, he says, but never together until now.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Aephraim Steinberg
Department of Physics
Centre for Quantum Information & Quantum Computing
University of Toronto
416-978-0713
Sean Bettam
Communications
Faculty of Arts & Science
University of Toronto
416-946-7950
Copyright © University of Toronto
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
![]() Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
Nanophotonic platform boosts efficiency of nonlinear-optical quantum teleportation April 25th, 2025
![]() Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Groundbreaking research unveils unified theory for optical singularities in photonic microstructures December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Quantum nanoscience
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








