Home > Press > Small tilt in magnets makes them viable memory chips
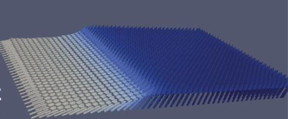 |
| This image taken from a computer simulation shows nanomagnets tilted at various angles, with the white regions indicating greater angles of tilt. Researchers have found that even a small tilt of 2 degrees will facilitate magnetic switching. CREDIT: Image by Samuel Smith, UC Berkeley |
Abstract:
University of California, Berkeley, researchers have discovered a new way to switch the polarization of nanomagnets, paving the way for high-density storage to move from hard disks onto integrated circuits.
Small tilt in magnets makes them viable memory chips
Berkeley, CA | Posted on August 3rd, 2015The advance, to be reported Monday, Aug. 3, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, could lead to computers that turn on in an instant and operate with far greater speed and significantly less power.
A research team led by Sayeef Salahuddin, an associate professor of electrical engineering and computer sciences, has found that a slight tilt of the magnets makes them easy to switch without an external magnetic field. This opens the door to a memory system that can be packed onto a microprocessor, a major step toward the goal of reducing energy dissipation in modern electronics.
"To reduce the power draw and increase the speed, we want to be able to manufacture a computer chip that includes memory so that it is close to the computational action," said Salahuddin. "However, the physics needed to create long-term storage are not compatible with integrated circuits."
Creating and switching polarity in magnets without an external magnetic field has been a key focus in the field of spintronics. Generating a magnetic field takes power and space, which is why magnets have not yet been integrated onto computer chips.
Instead, there are separate systems for long-term magnetic memory. These include a computer's hard disk drive where data are stored, and the various kinds of random-access memory, or RAM, on the integrated circuits of the central processing unit, or CPU, where calculations and logic operations are performed.
A large portion of the energy used in computing is spent on transferring data from one type of memory to another. Doing that quickly takes more energy and generates more heat.
In past research, Salahuddin and his colleagues found that directing electrical current through the rare metal tantalum creates polarity in magnets without an external magnetic field. But the battle wasn't over.
Packing a sufficient number of nanomagnets onto a chip meant aligning them perpendicularly, but that vertical orientation negated the switching effects of tantalum.
"We found that by tilting the magnet - just 2 degrees was enough - you get all the benefits of a high-density magnetic switch without the need for an external magnetic field," said Salahuddin.
###
The study's lead author is Long You, a research scholar in Salahuddin's lab.
The Department of Energy, National Science Foundation Center for Energy Efficient Electronics Science, and the Semiconductor Technology Advanced Research Network's Function Accelerated nanoMaterial Engineering Center (STARNET FAME) helped support this research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sarah Yang
510-643-7741
Copyright © University of California, Berkeley
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Memory Technology
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








