Home > Press > Scientists control the flow of heat and light in photonic crystals
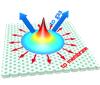 |
| Once the laser beam hits the surface of a sample it starts to generate heat which diffuses along the membrane but also it diffuses to the ambient gas. That effect reduces the width of the temperature distribution in the photonic crystal membrane. |
Abstract:
Scientists from the MESA+ Institute for Nanotechnology at the University of Twente in the Netherlands and Thales Research & Technology, France, have found a way to control heat propagation in photonic nano-sized devices, which will be used for high speed communications and quantum information technologies. Their results are published in the leading American journal Applied Physics Letters on 30 April 2015.
Scientists control the flow of heat and light in photonic crystals
Enschede, Netherlands | Posted on May 9th, 2015Heat controls light
Photonic crystals, are photonic structures with nano-sized geometrical features, are useful for the light control, for example, they can be used to make ultra-compact integrated circuits for light. One of the simplest and most versatile ways to control these circuits is by heating them, thereby locally changing their properties. However, it is extremely important to apply heat at the right place, but this is difficult because heat tends to diffuse. As a consequence neighboring elements will be affected by the heat, producing unwanted changes in structures with multiple elements. However, heat propagation in thin membranes also depends on the surrounding media, thus providing an extra degree of freedom to control the heat distribution.
Thus, the temperature distribution across the membrane can be reduced by changing the embedding medium. The faster the heat diffuses away, the narrower the temperature distribution is in the photonic crystal membrane.
The researchers experimentally and theoretically show that significantly better control is obtained using high thermal conductivity gases as the surrounding media. They found that when helium is used as the ambient gas, the width of the temperature distribution in the structure is reduced by 30% when compared to air. The results the researchers obtained are important because they enable thermal tuning of coupled resonators which will be valuable in the quest to build programmable optical circuits.
The research is founded by the European Research Council grant (№279248).
The paper
Applied Physics Letters, Vol. 106, p. 171113 (2015)
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jochem Vreeman
University of Twente
0031612221253
Sergei Sokolov, MSc.
University of Twente
Prof. Allard Mosk
University of Twente
Dr. Alfredo De Rossi
Thales Research & Technology
Copyright © University of Twente
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








