Home > Press > A spoonful of sugar in silver nanoparticles to regulate their toxicity
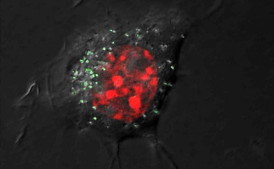 |
| This is a microscope image of a cell with silver nanoparticles with green fluorescence and red-stained nucleus. CREDIT: MPIKG |
Abstract:
The use of colloidal silver to treat illnesses has become more popular in recent years, but its ingestion, prohibited in countries like the US, can be harmful to health. Scientists from the Max Planck Institute in Germany have now confirmed that silver nanoparticles are significantly toxic when they penetrate cells, although the number of toxic radicals they generate can vary by coating them with carbohydrates.
A spoonful of sugar in silver nanoparticles to regulate their toxicity
Madrid, Spain | Posted on January 21st, 2015Silver salts have been used externally for centuries for their antiseptic properties in the treatment of pains and as a surface disinfectant for materials. There are currently people who use silver nanoparticles to make homemade potions to combat infections and illnesses such as cancer and AIDS, although in some cases the only thing they achieve is argyria or blue-tinged skin.
Health authorities warn that there is no scientific evidence that supports the therapeutic efficiency of colloidal silver and in fact, in some countries like the US, its ingestion is prohibited. On the contrary, there are numerous studies which demonstrate the toxicity of silver nanoparticles on cells.
One of these studies has just been published in the 'Journal of Nanobiotechnology' by an international team of researchers coordinated from the Max Planck Institute of Colloids and Interfaces (Germany). "We have observed that it is only when silver nanoparticles enter inside the cells that they produce serious harm, and that their toxicity is basically due to the oxidative stress they create," explains the Spanish chemist Guillermo Orts-Gil, project co-ordinator, to SINC.
To carry out the study, the team has analysed how different carbohydrates act on the surface of silver nanoparticles (Ag-NP) of around 50 nanometres, which have been introduced into cultures of liver cells and tumour cells from the nervous system of mice. The results reveal that, for example, the toxic effects of the Ag-NP are much greater if they are covered with glucose instead of galactose or mannose.
'Trojan horse' mechanism
Although not all the details on the complex toxicological mechanisms are known, it is known that the nanoparticles use a 'Trojan horse' mechanism to trick the membrane's defences and get inside the cell. "The new data shows how the different carbohydrate coatings regulate the way in which they do this, and this is hugely interesting for controlling their toxicity and designing future trials," points out Orts-Gil.
The researcher highlights that there is a "clear correlation between the coating of the nanoparticles, the oxidative stress and toxicity, and thus, these results open up new perspectives on regulating the bioactivity of the Ag-NP through the use of carbohydrates".
Silver nanoparticles are not only used to make homemade remedies; they are also increasingly used in drugs such as vaccines, as well as products such as clothes and cleaning cloths.
###
References:
David C Kennedy, Guillermo Orts-Gil*, Chian-Hui Lai, Larissa Müller, Andrea Haase, Andreas Luch, Peter H Seeberger. "Carbohydrate functionalization of silver nanoparticles modulates cytotoxicity and cellular uptake". Journal of Nanobiotechnology 12: 59, December 2014. Doi:10.1186/s12951-014-0059-z
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
SINC
34-914-251-820
Copyright © MPIKG
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Safety-Nanoparticles/Risk management
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
Onion-like nanoparticles found in aircraft exhaust May 14th, 2025
![]() Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
Closing the gaps — MXene-coating filters can enhance performance and reusability February 28th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








