Home > Press > Progress made in developing nanoscale electronics: New research directs charges through single molecules
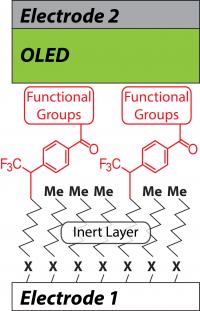 |
| A single layer of organic molecules connects the positive and negative electrodes in a molecular-junction OLED.
Credit: Graphic by Alexander Shestopalov/University of Rochester. |
Abstract:
Scientists are facing a number of barriers as they try to develop circuits that are microscopic in size, including how to reliably control the current that flows through a circuit that is the width of a single molecule.
Progress made in developing nanoscale electronics: New research directs charges through single molecules
Rochester, NY | Posted on April 21st, 2014Alexander Shestopalov, an assistant professor of chemical engineering at the University of Rochester, has done just that, thereby taking us one step closer to nanoscale circuitry.
"Until now, scientists have been unable to reliably direct a charge from one molecule to another," said Shestopalov. "But that's exactly what we need to do when working with electronic circuits that are one or two molecules thin."
Shestopalov worked with an OLED (organic light-emitting diode) powered by a microscopically small, simple circuit in which he connected a one-molecule thin sheet of organic material between positive and negative electrodes. Recent research publications have shown that it is difficult to control the current traveling through the circuit from one electrode to the other in such a thin circuit. As Shestopalov explains in a paper published in the journal Advanced Material Interfaces, the key was adding a second, inert layer of molecules.
The inert—or non-reactive—layer is made of a straight chain of organic molecules. On top a layer of aromatic—or ring-shaped—molecules acts like a wire conducting the electronic charge. The inert layer, in effect, acts like the plastic casing on electric wires by insulating and separating the live wires from the surrounding environment. Since the bottom layer is not capable of reacting with the overlapping layer, the electronic properties of the component are determined solely within the top layer.
The bi-layer arrangement also gave Shestopalov the ability to fine-tune his control of the charge transfer. By changing the functional groups—units of atoms that replace hydrogen in molecules and determine a molecule's characteristic chemical reactivity—he could more precisely affect the rate at which the current moved between the electrodes and the upper layer of organic molecules.
In molecular electronic devices, some functional groups accelerate the charge transfer, while others slow it down. By incorporating the inert layer of molecules, Shestopalov was able to reduce any interference with the top layer and, as a result, achieve the precise charge transfer needed in a device by changing the functional group.
For example, an OLED may need a faster charge transfer to maintain a specific luminescence, while a biomedical injection device may require a slower rate for delicate or variable procedures.
While Shestopalov overcame a significant obstacle, there remains a great deal of work to be done before bi-layer molecular electronic devices become practical. The next obstacle is durability.
"The system we developed degrades quickly at high temperatures," said Shestopalov. "What we need are devices that last for years, and that will take time to accomplish.
###
Shestopalov's research was funded by the National Science Foundation and University of Rochester ChemE Startup.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Peter Iglinski
585-273-4726
Copyright © University of Rochester
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanoelectronics
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








