Home > Press > Nanotube composites increase the efficiency of next generation of solar cells
 |
| The high degree of control of the method enables production of highly efficient nanotube networks with a very small amount of nanotubes compared to other conventional methods, thereby strongly reducing materials costs. |
Abstract:
Carbon nanotubes are becoming increasingly attractive for photovoltaic solar cells as a replacement to silicon. Researchers at Umeň University in Sweden have discovered that controlled placement of the carbon nanotubes into nano-structures produces a huge boost in electronic performance. Their groundbreaking results are published in the prestigious journal Advanced Materials.
Nanotube composites increase the efficiency of next generation of solar cells
Umeň, Sweden | Posted on March 18th, 2014Carbon nanotubes, CNTs, are one dimensional nanoscale cylinders made of carbon atoms that possess very unique properties. For example, they have very high tensile strength and exceptional electron mobility, which make them very attractive for the next generation of organic and carbon-based electronic devices.
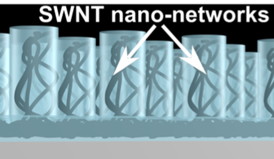
There is an increasing trend of using carbon based nanostructured materials as components in solar cells. Due to their exceptional properties, carbon nanotubes are expected to enhance the performance of current solar cells through efficient charge transport inside the device. However, in order to obtain the highest performance for electronic applications, the carbon nanotubes must be assembled into a well-ordered network of interconnecting nanotubes. Unfortunately, conventional methods used today are far from optimal which results in low device performance.
In a new study, a team of physicists and chemists at Umeň University have joined forces to produce nano-engineered carbon nanotubes networks with novel properties.
For the first time, the researchers show that carbon nanotubes can be engineered into complex network architectures, and with controlled nano-scale dimensions inside a polymer matrix.
"We have found that the resulting nano networks possess exceptional ability to transport charges, up to 100 million times higher than previously measured carbon nanotube random networks produced by conventional methods," says Dr David Barbero, leader of the project and assistant professor at the Department of Physics at Umeň University.
In a previous study (Applied Physics Letters, Volume 103, Issue 2, 021116 (2013)) the research team of David R. Barbero already demonstrated that nano-engineered networks can be produced onto thin and flexible transparent electrodes that can be used in flexible solar cells. These new results are expected to accelerate the development of next generation of flexible carbon based solar cells, which are both more efficient and less expensive to produce.
Editor: Ingrid S÷derbergh
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Barbero
46-070-210-7705
Copyright © Umea University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








