Home > Press > Discovery of first motor with revolution motion in a virus-killing bacteria advances nanotechnology
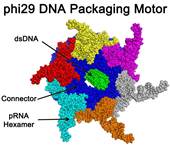 |
| Scientists have cracked a 35-year-old mystery about the workings of the natural motors that are models for development of a futuristic genre of synthetic nanomotors that pump therapeutic DNA, RNA or drugs into individual diseased cells.
Credit:Zhengyi Zhao |
Abstract:
Scientists have cracked a 35-year-old mystery about the workings of the natural motors that are serving as models for development of a futuristic genre of synthetic nanomotors that pump therapeutic DNA, RNA or drugs into individual diseased cells. Their report revealing the innermost mechanisms of these nanomotors in a bacteria-killing virus — and a new way to move DNA through cells — is being published online today in the journal ACS Nano.
Discovery of first motor with revolution motion in a virus-killing bacteria advances nanotechnology
Washington, DC | Posted on March 20th, 2013Peixuan Guo and colleagues explain that two motors have been found in nature: A linear motor and a rotating motor. Now they report discovery of a third type, a revolving molecular motor. Guo pointed out that nanomotors will open the door to practical machines and other nanotechnology devices so small that 100,000 would fit across the width of a human hair. One major natural prototype for those development efforts has been the motor that packages DNA into the shell of bacteriophage phi29, a virus that infects and kills bacteria. Guo's own research team wants to embed a synthetic version of that motor into nanomedical devices that are injected into the body, travel to diseased cells and pump in medication. A major barrier in doing so has been uncertainty and controversy about exactly how the phi29 motor moves. Scientists thought that it worked by rotating or spinning in the same motion as the Earth turning on its axis.
In their ACS Nano paper, Guo, with his team Zhengyi Zhao, Emil Khisamutdinov and Chad Schwartz, challenges that idea. Indeed, they discovered that the phi29 motor moves DNA without any rotational motion. The motor moves DNA with a revolving in the same motion as the Earth revolving around the sun. "The revolution without rotation model could resolve a big conundrum troubling the past 35 years of painstaking investigation of the mechanism of these viral DNA packaging motors," the report states.
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering, National Institutes of Health.
####
About American Chemical Society (ACS)
The American Chemical Society is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. With more than 163,000 members, ACS is the world's largest scientific society and a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related research through its multiple databases, peer-reviewed journals and scientific conferences. Its main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Peixuan Guo, Ph.D.
William Farish Endowed Chair in Nanobiotechnology
School of Pharmacy, University of Kentucky
565 Biopharmaceutical Complex
789 S. Limestone Street
Lexington, Ky. 40536
Phone: 859-218-0128 (office); 513-728-1411 (cell)
Copyright © American Chemical Society (ACS)
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Illustrated videos of the mechanism can be found at:
Illustrated videos of the mechanism can be found at:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Videos/Movies
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Molecular Nanotechnology
![]() Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
Quantum pumping in molecular junctions August 16th, 2024
![]() Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
Scientists push the boundaries of manipulating light at the submicroscopic level March 3rd, 2023
![]() First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
First electric nanomotor made from DNA material: Synthetic rotary motors at the nanoscale perform mechanical work July 22nd, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








