Home > Press > ORNL pushes the boundaries of electron microscopy to unlock the potential of graphene
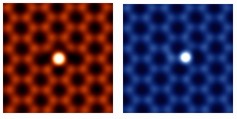 |
| The atomic resolution Z-contrast images show individual silicon atoms bonded differently in graphene. |
Abstract:
Electron microscopy at the Department of Energy's Oak Ridge National Laboratory is providing unprecedented views of the individual atoms in graphene, offering scientists a chance to unlock the material's full potential for uses from engine combustion to consumer electronics.
ORNL pushes the boundaries of electron microscopy to unlock the potential of graphene
Oak Ridge, TN | Posted on November 16th, 2012 Graphene crystals were first isolated in 2004. They are two-dimensional (one-atom in thickness), harder than diamonds and far stronger than steel, providing unprecedented stiffness, electrical and thermal properties. By viewing the atomic and bonding configurations of individual graphene atoms, scientists are able to suggest ways to optimize materials so they are better suited for specific applications.
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters, a team of researchers from Oak Ridge National Laboratory and Vanderbilt University used aberration-corrected scanning transmission electron microscopy to study the atomic and electronic structure of silicon impurities in graphene.
"We have used new experimental and computational tools to reveal the bonding characteristics of individual impurities in graphene. For instance, we can now differentiate between a non-carbon atom that is two-dimensionally or three-dimensionally bonded in graphene. In fact, we were finally able to directly visualize a bonding configuration that was predicted in the 1930s but has never been observed experimentally," said ORNL researcher Juan-Carlos Idrobo. Electrons in orbit around an atom fall into four broad categories - s, p, d and f - based on factors including symmetry and energy levels.
"We observed that silicon d-states participate in the bonding only when the silicon is two-dimensionally coordinated," Idrobo said. "There are many elements such as chromium, iron, and copper where the d-states or d-electrons play a dominant role in determining how the element bonds in a material."
By studying the atomic and electronic structure of graphene and identifying any impurities, researchers can better predict which elemental additions will improve the material's performance.
Slightly altering the chemical makeup of graphene could customize the material, making it more suitable for a variety of applications. For example, one elemental addition may make the material a better replacement for the platinum catalytic converters in cars, while another may allow it to function better in electronic devices or as a membrane.
Graphene has the potential to replace the inner workings of electronic gadgets people use every day because of its ability to conduct heat and electricity and its optical transparency. It offers a cheaper and more abundant alternative to indium, a limited resource that is widely used in the transparent conducting coating present in almost all electronic display devices such as digital displays in cars, TVs, laptops and handheld gadgets like cell phones, tablets and music players.
Researchers expect the imaging techniques demonstrated at ORNL to be used to understand the atomic structures and bonding characteristics of atoms in other two-dimensional materials, too.
The authors of the paper are Wu Zhou, Myron Kapetanakis, Micah Prange, Sokrates Pantelides, Stephen Pennycook and Idrobo.
This research was supported by National Science Foundation and the DOE Office of Science. Researchers also made use of Oak Ridge National Laboratory's Shared Research Equipment User Facility along with Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory's National Energy Research Scientific Computing Center, both of which are also supported by DOE's Office of Science.
####
About DOE/Oak Ridge National Laboratory
ORNL is managed by UT-Battelle for the Department of Energy's Office of Science. DOE's Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States, and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit science.energy.gov.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jennifer Brouner
865-241-9515
Copyright © DOE/Oak Ridge National Laboratory
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Laboratories
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
First real-time observation of two-dimensional melting process: Researchers at Mainz University unveil new insights into magnetic vortex structures August 8th, 2025
![]() Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
Researchers unveil a groundbreaking clay-based solution to capture carbon dioxide and combat climate change June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Automotive/Transportation
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








