Home > Press > A New Playground for Particle Design
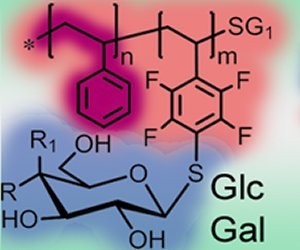 |
| Researchers from the University of Jena (Germany) designed glycopolymeric materials with tailored properties to independently study the parameters that impact cellular uptake. |
Abstract:
Synthetic polymers offer the possibility to introduce biologically active moieties and to design tailor-made macromolecules with well-defined architectures and properties. The design of glycopolymeric materials with tailored properties has become a very important topic of interest in current chemistry, biology, and medicine.
A New Playground for Particle Design
Germany | Posted on August 10th, 2012The main reason behind this significance lies within their structure. A glycopolymer, by definition, consists of a synthetic polymeric backbone with covalently-linked, pendant carbohydrate moieties. The backbone may be composed of various monomeric units, in different arrangements. As a consequence, it provides the possibility to adjust the physical properties, such as water solubility of the final material.
The second building block of a glycopolymer consists of pendant sugar moieties which act as ligands for a broad spectrum of protein receptors that play an important role in different cell-surface interactions. Therefore, the structure of synthetic glycopolymers allows the precise modification of their material and biological features for special biomedical purposes.
Now, the research group around Ulrich Schubert (University of Jena) have demonstrated that poly(pentafluorostyrene)-based glycopolymers also possess the above-mentioned properties. By the introduction of hydrophobic polystyrene block into the backbone they can modify the water solubility of the system and obtain amphiphilic glycopolymers. These materials do not dissolve in aqueous environments. Under appropriate conditions they form nanoparticles with carbohydrates on the surface. By the introduction of glucose or galactose the recognition and uptake of these polymers by liver cancer cells is modified.
Fluorescence microscopy and flow cytometry show that nanoparticles are taken up by these cells to a higher degree than respective water soluble polymers, and that internalization of galactosylated materials is enhanced. These glycopolymers can find a multitude of potential applications in, for example, liver tumor-targeted chemotherapy, imaging, and as extracellular matrices for hepatocytes.
####
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Wiley-VCH Materials Science Journals
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
Link to the original paper on Wiley Online Library:
| Related News Press |
Chemistry
![]() Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
Projecting light to dispense liquids: A new route to ultra-precise microdroplets January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








