Home > Press > Electric charge disorder: A key to biological order? Strong attraction that arises between biological objects with random patches of electric charge on an otherwise neutral surface may partly explain pattern recognition in biology
 |
Abstract:
Theoretical physicist Ali Naji from the IPM in Tehran and the University of Cambridge, UK, and his colleagues have shown how small random patches of disordered, frozen electric charges can make a difference when they are scattered on surfaces that are overall neutral. These charges induce a twisting force that is strong enough to be felt as far as nanometers or even micrometers away. These results, about to be published in EPJ E¹, could help to understand phenomena that occurr on surfaces such as those of large biological molecules.
Electric charge disorder: A key to biological order? Strong attraction that arises between biological objects with random patches of electric charge on an otherwise neutral surface may partly explain pattern recognition in biology
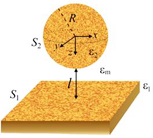
Tehran, Iran and Cambridge, UK | Posted on April 30th, 2012To measure the strength of the twist that acts on a randomly charged surface, the authors used a sphere which was mounted like a spinning top next to a randomly charged flat substrate. Because small amounts of positive and negative charges were spread in a disordered mosaic throughout both surfaces, they induced transient attractive or repulsive twisting forces. This was regardless of the surfaces' overall electrical neutrality, thus making the sphere spin. Using statistical averaging methods, the authors studied the fluctuations of these forces.
The authors found that the twisting force, created by virtue of the disorder of surface charges, is expected to be much stronger and far-reaching than the remnant forces. The latter are always present, even in the absence of charge disorder, and are due to fluctuations at the atomic and molecular levels.
This could have implications for large randomly charged surfaces such as biological macromolecules, which may be exposed to strong electrostatic forces, inducing attraction and/or repulsion, even if they carry no overall net charge. For instance, this phenomenon could partly explain biological pattern recognition, such as lock and key phenomena. In that context, the twisting force could explain the attraction between biological macromolecules that lead to pre-alignment prior to their interaction.
Reference:
1. Naji A., Sarabadani J., Dean D.S., and Podgornik R. (2012), Sample-to-sample torque fluctuations in a system of coaxial randomly charged surfaces, European Physical Journal E (EPJ E). DOI 10.1140/epje/i2012-12024-y
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Janine Haubenreisser
49-622-148-78414
Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Visit the homepage of the European Physical Journal:
Visit the homepage of the European Physical Journal:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Physics
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Magnetism in new exotic material opens the way for robust quantum computers June 4th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








