Home > Press > American Chemical Society Podcast: Tiny generator powers wireless device
 |
Abstract:
Imagine a new genre of tiny implantable sensors, airborne and stationary surveillance cameras and sensors and other devices that operate without batteries on energy collected from the motion of a heart beat and have wireless communications capability. And the power plant for those devices is a "nanogenerator" that could even produce energy to charge an iPod from the movements of a person walking down the street.
American Chemical Society Podcast: Tiny generator powers wireless device
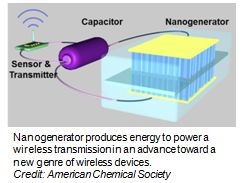
Washington, DC | Posted on June 29th, 2011That's the topic of a new episode in the American Chemical Society's (ACS) award-winning "Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions" podcast series, which was released today. The podcast features Zhong Lin Wang, Ph.D., of the Georgia Institute of Technology who, described development of the first practical iteration of the device. Wang and colleagues boosted the power output of earlier devices by thousands of times and its voltage by 150 times. Wang reported on the achievement at an ACS National Meeting held in March in Anaheim, Calif.
And the news gets even better. In a development just reported in the ACS journal Nano Letters, Wang and his colleagues also showed for the first time that they could integrate such a nanogenerator into an electronic circuit. It can transmit data wirelessly to an ordinary commercial radio at distances up to 30 feet. The generator can produce electricity using energy from a gentle breeze, movements of a person walking and other sources to power those wireless data transmissions.
"This development represents a milestone toward producing portable electronics that can be powered by body movements without the use of batteries or electrical outlets," Wang says in the podcast. "Our nanogenerators are poised to change lives in the future. Their potential is only limited by one's imagination."
####
About American Chemical Society (ACS)
The nanogenerator may find a broad range of other applications that require more power, according to Wang. He lists, for example, personal electronic devices powered by footsteps activating nanogenerators inside the sole of a shoe; implanted insulin pumps powered by a heartbeat; and environmental sensors powered by nanogenerators flapping in the breeze.
The new podcast is available without charge at iTunes and from ACS’ website at www.acs.org/globalchallenges.
Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions is a series of podcasts describing some of the 21st Century’s most daunting problems, and how cutting-edge research in chemistry matters in the quest for solutions. Global Challenges is the centerpiece in an alliance on sustainability between ACS and the Royal Society of Chemistry. Global Challenges is a sweeping panorama of global challenges that includes dilemmas such as providing a hungry, thirsty world with ample supplies of safe food and clean water; developing alternatives to petroleum to fuel society; preserving the environment and assuring a sustainable future for our children; and improving human health. During the 2011 global celebration of the International Year of Chemistry (IYC), Global Challenges/Chemistry Solutions also is focusing on the main themes of IYC — health, environment, energy, and materials.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Michael Bernstein
202-872-6042
Michael Woods
202-872-6293
Copyright © American Chemical Society
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Battery Technology/Capacitors/Generators/Piezoelectrics/Thermoelectrics/Energy storage
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
![]() MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
MXene nanomaterials enter a new dimension Multilayer nanomaterial: MXene flakes created at Drexel University show new promise as 1D scrolls January 30th, 2026
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








