Home > Press > Nanosponge drug delivery system more effective than direct injection
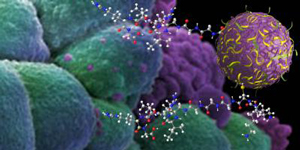 |
| The illustration shows a nanosponge particle attaching to human breast cancer cells. The particle holds an anticancer drug that it releases gradually as it decomposes. Peptide linkers are shown with the ball and stick representation. Although only two are shown in the illustration, about three dozen are attached to the surface of actual particles. The linkers are specially configured to bind to the surface of irradiated cancer cells. Credit: Harth Laboratory. |
Abstract:
When loaded with an anticancer drug, a delivery system based on a novel material called nanosponge is three to five times more effective at reducing tumor growth than direct injection.
That is the conclusion of a paper published in the June 1 issue of the journal Cancer Research.
By David F. Salisbury
Nanosponge drug delivery system more effective than direct injection
Nashville, TN | Posted on June 4th, 2010"Effective targeted drug delivery systems have been a dream for a long time now but it has been largely frustrated by the complex chemistry that is involved," says Eva Harth, assistant professor of chemistry at Vanderbilt, who developed the nanosponge delivery system. "We have taken a significant step toward overcoming these obstacles."
The study was a collaboration between Harth's laboratory and that of Dennis E. Hallahan, a former professor of radiation oncology at Vanderbilt who is now at the Washington University School of Medicine. Corresponding authors are Harth and Roberto Diaz at Emory University, who was working in the Hallahan laboratory when the studies were done.
To visualize Harth's delivery system, imagine making tiny sponges that are about the size of a virus, filling them with a drug and attaching special chemical "linkers" that bond preferentially to a feature found only on the surface of tumor cells and then injecting them into the body. The tiny sponges circulate around the body until they encounter the surface of a tumor cell where they stick on the surface (or are sucked into the cell) and begin releasing their potent cargo in a controllable and predictable fashion.
Targeted delivery systems of this type have several basic advantages: Because the drug is released at the tumor instead of circulating widely through the body, it should be more effective for a given dosage. It should also have fewer harmful side effects because smaller amounts of the drug come into contact with healthy tissue.
"We call the material nanosponge, but it is really more like a three-dimensional network or scaffold," says Harth. The backbone is a long length of polyester. It is mixed in solution with small molecules called cross-linkers that act like tiny grappling hooks to fasten different parts of the polymer together. The net effect is to form spherically shaped particles filled with cavities where drug molecules can be stored. The polyester is biodegradable, so it breaks down gradually in the body. As it does, it releases the drug it is carrying in a predictable fashion.
"Predictable release is one of the major advantages of this system compared to other nanoparticle delivery systems under development," says Harth. When they reach their target, many other systems unload most of their drug in a rapid and uncontrollable fashion. This is called the burst effect and makes it difficult to determine effective dosage levels.
Another major advantage is that the nanosponge particles are soluble in water. Encapsulating the anti-cancer drug in the nanosponge allows the use of hydrophobic drugs that do not dissolve readily in water. Currently, these drugs must be mixed with another chemical, called an adjuvant reagent, that reduces the efficacy of the drug and can have adverse side-effects.
It is also possible to control the size of nanosponge particles. By varying the proportion of cross-linker to polymer, the nanosponge particles can be made larger or smaller. This is important because research has shown that drug delivery systems work best when they are smaller than 100 nanometers, about the depth of the pits on the surface of a compact disc. The nanosponge particles used in the current study were 50 nanometers in size. "The relationship between particle size and the effectiveness of these drug delivery systems is the subject of active investigation," says Harth.
The other major advantage of Harth's system is the simple chemistry required. The researchers have developed simple, high-yield "click chemistry" methods for making the nanosponge particles and for attaching the linkers, which are made from peptides, relatively small biological molecules built by linking amino acids. "Many other drug delivery systems require complicated chemistry that will be difficult to scale up for commercial production, but we have continually kept this in mind," Harth says.
The targeting peptide used in the animal studies was developed by the Hallahan laboratory, which also tested the system's effectiveness in tumor-bearing mice. The peptide used in the study is one that selectively binds to tumors that have been treated with radiation.
The drug used for the animal studies was paclitaxel (the generic name of the drug Taxol) that is used in cancer chemotherapy. The researchers recorded the response of two different tumor types - slow-growing human breast cancer and fast-acting mouse glioma - to single injections. In both cases they found that it increased the death of cancer cells and delayed tumor growth "in a manner superior to know chemotherapy approaches."
The next step is to perform an experiment with repeated injections to see if the nanosponge system can stop and reverse tumor growth. Harth is also planning to perform the more comprehensive toxicity studies on her nanoparticle delivery system that are required before it can be used in clinical trials.
Additional participants in the study were Ralph J. Passarella, Daniel E. Spratt, John G. Phillips, Hongmei Wu and Li Zhou from the Vanderbilt University Medical Center and Alice E. van der Ende and Vasanth Sathiyakumar from Vanderbilt's Department of Chemistry.
The research was supported by grants from the Department of Defense, National Science Foundation and National Institutes of Health.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David F. Salisbury
(615) 322-NEWS
Copyright © Vanderbilt University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Academic/Education
![]() Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
Rice University launches Rice Synthetic Biology Institute to improve lives January 12th, 2024
![]() Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Multi-institution, $4.6 million NSF grant to fund nanotechnology training September 9th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








