Home > Press > New Nanopore Technique Facilitates Faster, Cheaper Genome Analyses
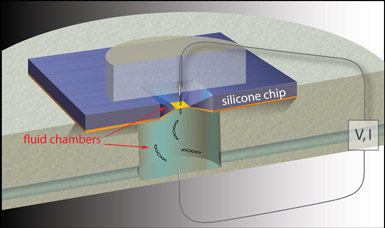 |
| Schematic of a solid state nanopore used for genome analyses (not to scale). The electrostatic potential near an approximately five nanometer-wide, solid-state nanopore attracts negatively-charged, double-stranded DNA molecules into the pore, which electronically detects the molecules as they traverse the pore. (Photo courtesy of Nature Nanotechnology.) |
Abstract:
Ultra-fast, low-cost genomic sequencing and profiling may some day accelerate the pace of biological discovery and enable clinicians to quickly and precisely diagnose patients' susceptibility to disease and tolerance of selected drugs. But this scenario may not be realized until engineers find a way to considerably increase the sensitivity of sensors used to detect the DNA molecules that define the human genome.
New Nanopore Technique Facilitates Faster, Cheaper Genome Analyses
Boston, MA | Posted on December 21st, 2009It's a feat that could be achieved by reducing the number of target DNA molecule copies needed to obtain an accurate read. And that presents a formidable challenge: to produce sufficient copies to decipher the genome using current technology, most scientists still rely on time-consuming, expensive, and error-prone DNA replication tools such as the polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Now researchers have devised a method that advances the prospects for efficiently analyzing DNA samples without amplification. In a study published in the Dec. 20 online edition of Nature Nanotechnology, Associate Professor Amit Meller (BME, Physics), BME postdoctoral fellow Meni Wanunu, BU physics student Will Morrison and collaborators at New York University and Bar-Ilan University demonstrated a method to tune solid-state nanopores — tiny, nearly cylindrical, silicon nitride sensors that electronically detect DNA molecules as they pass through the pore — to require far fewer DNA molecules than ever before.
"This study shows that using our method, we can detect a much smaller amount of DNA than previously published," said Meller. "When people will start to implement genome sequencing or profiling using nanopores, they could use our nanopore capture approach to greatly reduce the number of copies used in those measurements."
Nanopore capture consists of two distinct steps: the arrival of a sample molecule to the pore mouth, and the threading of the end of that molecule into the pore. To significantly increase the rate at which nanopores capture incoming, two nanometer-wide DNA molecules, Meller and his colleagues used salt gradients to alter the electric field in the pore's vicinity. This achieved a funneling effect that directed charged DNA molecules toward the mouth of the pore and boosted the molecules' arrival and threading rates.
By upping the capture rate by a few orders of magnitude and decreasing the volume of the sample receiving chamber, the researchers reduced the number of DNA molecule copies required for nanopore-based detection by a factor of 10,000 — from about one billion sample molecules to 100,000. They also demonstrated that longer DNA molecules (containing tens of thousands of nucleotide base pairs) increased the capture rate even further.
"PCR and other DNA replication technologies limit DNA molecule length," said Meller. "Because our method avoids amplification, it not only reduces the cost, time and error rate of DNA replication techniques, but also enables the analysis of very long strands of DNA."
Funded by the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation, the research team set out to achieve a better understanding of the physical forces that govern the DNA capture process. They arrived at their findings by using high-end transmission electron microscopes (TEM) to fabricate hundreds of nanopores with atomic-scale precision, and testing differently configured salt gradients near the pores.
"We had to perform extensive studies with these nearly atomic-scale pores in order to reveal how the electrostatic potential, which extends at least hundreds of nanometers away from the pore, focuses DNA into and through the pore," said Meller.
To conduct further investigations of unamplified genomes, Meller is now exploring other technologies, including optical detection and force measurements, for reading single DNA molecules as they pass through nanopores.
####
About Boston University
Boston University is one of the leading private research and teaching institutions in the world today, with two primary campuses in the heart of Boston and programs around the world.
For more information, please click here
Copyright © Boston University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Nanomedicine
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
Cambridge chemists discover simple way to build bigger molecules – one carbon at a time June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Sensors
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Tools
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
New molecular technology targets tumors and simultaneously silences two ‘undruggable’ cancer genes August 8th, 2025
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
Ben-Gurion University of the Negev researchers several steps closer to harnessing patient's own T-cells to fight off cancer June 6th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








