Home > Press > Penn materials scientist finds plumber's wonderland on graphene
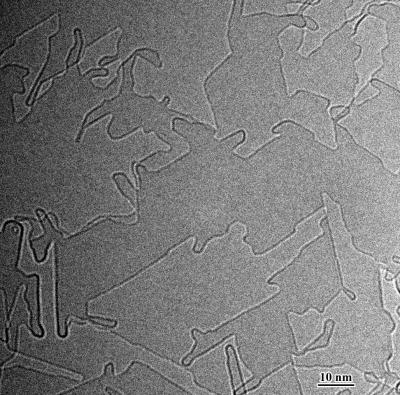 |
| This is an electron micrograph showing the formation of interconnected carbon nanostructures on a graphene substrate, which may be harnessed to make future electronic devices.
Credit: Ju Li and the University of Pennsylvania |
Abstract:
Engineers from the University of Pennsylvania, Sandia National Laboratories and Rice University have demonstrated the formation of interconnected carbon nanostructures on graphene substrate in a simple assembly process that involves heating few-layer graphene sheets to sublimation using electric current that may eventually lead to a new paradigm for building integrated carbon-based devices.
Penn materials scientist finds plumber's wonderland on graphene
Philadelphia, PA | Posted on June 12th, 2009Curvy nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes and fullerenes have extraordinary properties but are extremely challenging to pick up, handle and assemble into devices after synthesis. Penn materials scientist Ju Li and Sandia scientist Jianyu Huang have come up with a novel idea to construct curvy nanostructures directly integrated on graphene, taking advantage of the fact that graphene, an atomically thin two-dimensional sheet, bends easily after open edges have been cut on it, which can then fuse with other open edges permanently, like a plumber connecting metal fittings.
The "knife" and "welding torch" used in the experiments, which were performed inside an electron microscope, was electrical current from a Nanofactory scanning probe, generating up to 2000°C of heat. Upon applying the electrical current to few-layer graphene, they observed the in situ creation of many interconnected, curved carbon nanostructures, such as "fractional nanotube"-like graphene bi-layer edges, or BLEs; BLE rings on graphene equivalent to "anti quantum-dots"; and nanotube-BLE assembly connecting multiple layers of graphene.
Remarkably, researchers observed that more than 99 percent of the graphene edges formed during sublimation were curved BLEs rather than flat monolayer edges, indicating that BLEs are the stable edges in graphene, in agreement with predictions based on symmetry considerations and energetic calculations. Theory also predicts these BLEs, or "fractional nanotubes," possess novel properties of their own and may find applications in devices.
The study is published in the current issue of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. Short movies of the fabrication of these nanostructures can be viewed at www.youtube.com/user/MaterialsTheory.
Li and Huang observed the creation of these interconnected carbon nanostructures using the heat of electric current and a high-resolution transmission electron microscope. The current, once passed through the graphene layers, improved the crystalline quality and surface cleanness of the graphene as well, both important for device fabrication.
The sublimation of few-layer graphene, such as a 10-layer stack, is advantageous over the sublimation of monolayers. In few-layer graphene, layers spontaneously fuse together forming nanostructures on top of one or two electrically conductive, extended, graphene sheets.
During heating, both the flat graphene sheets and the self-wrapping nanostructures that form, like bilayer edges and nanotubes, have unique electronic properties important for device applications. The biggest obstacle for engineers has been wrestling control of the structure and assembly of these nanostructures to best exploit the properties of carbon. The discoveries of self-assembled novel carbon nanostructures may circumvent the hurdle and lead to new approach of graphene-based electronic devices.
Researchers induced the sublimation of multilayer graphene by Joule-heating, making it thermodynamically favorable for the carbon atoms at the edge of the material to escape into the gas phase, leaving freshly exposed edges on the solid graphene. The remaining graphene edges curl and often welded together to form BLEs. Researchers attribute this behavior to nature's driving force to reduce capillary energy, dangling bonds on the open edges of monolayer graphene, at the cost of increased bending energy.
"This study demonstrates it is possible to make and integrate curved nanostructures directly on flat graphene, which is extended and electrically conducting," said Li, associate professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering in Penn's School of Engineering and Applied Science. "Furthermore, it demonstrates that multiple graphene sheets can be intentionally interconnected. And the quality of the plumbing is exceptionally high, better than anything people have used for electrical contacts with carbon nanotubes so far. We are currently investigating the fundamental properties of graphene bi-layer edges, BLE rings and nanotube-BLE junctions."
The study was performed by Li and Liang Qi of Penn, Jian Yu Huang and Ping Lu of the Center for Integrated Nanotechnologies at Sandia and Feng Ding and Boris I. Yakobson of the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Materials Science at Rice.
It was supported by the National Science Foundation, the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Honda Research Institute, the Department of Energy and the Office of Naval Research.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Jordan Reese
215-573-6604
Copyright © University of Pennsylvania
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Nanotubes/Buckyballs/Fullerenes/Nanorods/Nanostrings/Nanosheets
![]() Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
Tiny nanosheets, big leap: A new sensor detects ethanol at ultra-low levels January 30th, 2026
![]() Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
Enhancing power factor of p- and n-type single-walled carbon nanotubes April 25th, 2025
![]() Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
Chainmail-like material could be the future of armor: First 2D mechanically interlocked polymer exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength January 17th, 2025
![]() Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Innovative biomimetic superhydrophobic coating combines repair and buffering properties for superior anti-erosion December 13th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Quantum Dots/Rods
![]() A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
A new kind of magnetism November 17th, 2023
![]() IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
IOP Publishing celebrates World Quantum Day with the announcement of a special quantum collection and the winners of two prestigious quantum awards April 14th, 2023
![]() Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
Qubits on strong stimulants: Researchers find ways to improve the storage time of quantum information in a spin rich material January 27th, 2023
![]() NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
NIST’s grid of quantum islands could reveal secrets for powerful technologies November 18th, 2022
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








