Home > Press > Columbia Researchers Squeeze Light into Nanoscale Devices and Circuits: Team is first to directly image propagation and dynamics of graphene plasmons at very low temperatures; findings could impact optical communications and signal processing
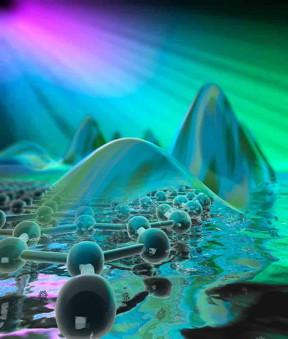 |
| The best pictorial representation of a surface plasmon polariton is in terms of a “ripple” of electron density on the surface of graphene sample. Dmitri Basov/Columbia University |
Abstract:
As electronic devices and circuits shrink into the nanoscale, the ability to transfer data on a chip, at low power with little energy loss, is becoming a critical challenge. Over the past decade, squeezing light into tiny devices and circuits has been a major goal of nanophotonics researchers. Electronic oscillations at the surface of metals, known as surface plasmon polaritons or plasmons for short, have become an intense area of focus. Plasmons are hybrids of light (photons) and electrons in a metal. If researchers can harness this nanolight, they will be able to improve sensing, subwavelength waveguiding, and optical transmission of signals.
Columbia Researchers Squeeze Light into Nanoscale Devices and Circuits: Team is first to directly image propagation and dynamics of graphene plasmons at very low temperatures; findings could impact optical communications and signal processing
New York, NY | Posted on May 23rd, 2018Columbia investigators have made a major breakthrough in this research, with their invention of a novel “home-built” cryogenic near-field optical microscope that has enabled them to directly image, for the first time, the propagation and dynamics of graphene plasmons at variable temperatures down to negative 250 degrees Celsius. The study was published online today in Nature.
“Our temperature-dependent study now gives us direct physical insight into the fundamental physics of plasmon propagation in graphene,” says Dimitri N. Basov, professor of physics at Columbia University, who led the study together with colleagues Cory Dean (physics) and James Hone (mechanical engineering, Columbia Engineering). “This insight was impossible to attain in previous nanoimaging studies done at room temperature. We were particularly surprised at discovering, after many years of failed attempts to get anywhere close, that compact nanolight can travel along the surface of graphene for distances of many tens of microns without unwanted scattering. The physics limiting the travel range of nanolight is a fundamental finding of our study and may lead to new applications in sensors, imaging, and signal processing.”
Basov, Dean, and Hone bring together years of experience in working with graphene, the one-atom-thick material that is one of the most promising candidates for novel photonic materials. Graphene’s optical properties are readily tunable and can be altered at ultrafast time scales. However, implementing nanolight without introducing unwanted dissipation in graphene has been very difficult to achieve.
The Columbia researchers developed a practical approach to confining light to the nanoscale. They knew they could form plasmon-polaritons, or resonant modes, in the graphene that propagate through the material as hybrid excitations of light and mobile electrons. These plasmon-polariton modes can confine the energy of electromagnetic radiation, or light, down to the nanoscale. The challenge was how to visualize these waves with ultra-high spatial resolution, so that they could study the performance of plasmonic modes at varying temperatures.
Alexander S. McLeod, a postdoctoral research scientist in the Basov Nano-optics Laboratory, built a unique microscope that enabled the team to explore the plasmon-polariton waves at high resolution while they cooled the graphene to cryogenic temperatures. Lowering the temperatures allowed them to “turn off” various scattering, or dissipation, mechanisms, one after another, as they cooled down their samples and learned which mechanisms were relevant.
“Now that our novel nanoimaging capabilities are deployed to low temperatures, we can see directly the unmitigated wave propagation of collective light-and-charge excitations within graphene,” says McLeod, co-lead author of the study with Guangxin Ni, also a postdoctoral research scientist in Basov’s lab. “Often times in physics, as in life, seeing truly is believing! The record-breaking travel range of these waves shows they’re destined to take on a life of their own, funneling signals and information back and forth inside next-generation optical devices.”
The study is the first to demonstrate the fundamental limitations for the propagation of plasmon polariton waves in graphene. The team found that graphene plasmons propagate ballistically, across tens of micrometers, throughout the tiny device. These plasmon modes are confined within a volume of space hundreds, if not thousands, of times smaller than that occupied by freely propagating light.
Plasmons in graphene can be tuned and controlled via an external electric field, which gives graphene a big advantage over conventional plasmonic media such as metal surfaces, which are inherently non-tunable. Moreover, the lifetimes of plasmon waves in graphene are now found to exceed those in metals by a factor of 10 to a 100, while propagating over comparably longer distances. These features offer enormous advantages for graphene as a plasmonic medium in next-generation opto-electronic circuits.
“Our results establish that graphene ranks among the best candidate materials for infrared plasmonics, with applications in imaging, sensing, and nano-scale manipulation of light,” says Hone. “Furthermore, our findings reveal the fundamental physics of processes that limit propagation of plasmon waves in graphene. This monumental insight will guide future efforts in nanostructure engineering, which may be able to remove the remaining roadblocks for long-range travel of versatile nanoconfined light within future optical devices.”
The current study is the beginning of a series of low-temperature investigations focused on controlling and manipulating confined plasmons in nanoscale optoelectronic graphene devices. The team is now using low-temperature nanoimaging to explore novel plasmonics effects such as electrically-induced plasmonic reflection and modulation, topological chiral plasmons, and also superconducting plasmonics in the very recently discovered “magic angle” system of twisted bilayer graphene.
####
About Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science
Columbia Engineering, based in New York City, is one of the top engineering schools in the U.S. and one of the oldest in the nation. Also known as The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, the School expands knowledge and advances technology through the pioneering research of its more than 200 faculty, while educating undergraduate and graduate students in a collaborative environment to become leaders informed by a firm foundation in engineering. The School’s faculty are at the center of the University’s cross-disciplinary research, contributing to the Data Science Institute, Earth Institute, Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute, Precision Medicine Initiative, and the Columbia Nano Initiative. Guided by its strategic vision, “Columbia Engineering for Humanity,” the School aims to translate ideas into innovations that foster a sustainable, healthy, secure, connected, and creative humanity.Columbia Engineering, based in New York City, is one of the top engineering schools in the U.S. and one of the oldest in the nation. Also known as The Fu Foundation School of Engineering and Applied Science, the School expands knowledge and advances technology through the pioneering research of its more than 200 faculty, while educating undergraduate and graduate students in a collaborative environment to become leaders informed by a firm foundation in engineering. The School’s faculty are at the center of the University’s cross-disciplinary research, contributing to the Data Science Institute, Earth Institute, Zuckerman Mind Brain Behavior Institute, Precision Medicine Initiative, and the Columbia Nano Initiative. Guided by its strategic vision, “Columbia Engineering for Humanity,” the School aims to translate ideas into innovations that foster a sustainable, healthy, secure, connected, and creative humanity.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Holly Evarts
Director of Strategic Communications and Media Relations
212-854-3206 (o)
347-453-7408 (c)
Copyright © Columbia University School of Engineering and Applied Science
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Plasmonics
![]() A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
A new dimension in magnetism and superconductivity launched November 5th, 2021
![]() Patterning silicon at the one nanometer scale: Scientists engineer materials’ electrical and optical properties with plasmon engineering August 13th, 2021
Patterning silicon at the one nanometer scale: Scientists engineer materials’ electrical and optical properties with plasmon engineering August 13th, 2021
![]() TPU scientists offer new plasmon energy-based method to remove CO2 from atmosphere March 19th, 2021
TPU scientists offer new plasmon energy-based method to remove CO2 from atmosphere March 19th, 2021
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








