Home > Press > Most Complex Nanoparticle Crystal Ever Made by Design: Possible applications include controlling light, capturing pollutants, delivering therapeutics
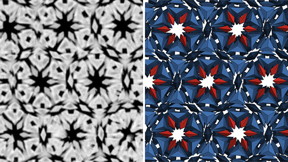 |
| The most complex crystal designed and built from nanoparticles. Left: An electron microscope image of a slice of the structure (Northwestern University). Right: A matching slice from a simulation of the structure (University of Michigan). |
Abstract:
•New crystal nanostructures are far more complex than others
•Tour de force demonstration of controlling nanoparticle shape and connections
•Researchers use DNA in smart way to build the complex crystal structures
Most Complex Nanoparticle Crystal Ever Made by Design: Possible applications include controlling light, capturing pollutants, delivering therapeutics
Evanston, IL | Posted on March 2nd, 2017The most complex crystal designed and built from nanoparticles has been reported by researchers at Northwestern University and the University of Michigan. The work demonstrates that some of nature’s most complicated structures can be deliberately assembled if researchers can control the shapes of the particles and the way they connect using DNA.
“This is a tour de force demonstration of what is possible when one harnesses the chemistry of DNA and combines it with nanoparticles whose shapes encourage a particular crystal structure,” said Chad A. Mirkin, the George B. Rathmann Professor of Chemistry in the Weinberg College of Arts and Sciences at Northwestern.
Nanotechnology promises to bring materials together in new ways, forging new capabilities by design. One potential application for crystals built of nanoparticles, such as these newly reported ones, is the control of light -- nanoparticles interact well with light waves because they are similar in size. This could lead to materials that can change colors or patterns on command or block certain wavelengths of light, while transmitting or amplifying others. New types of lenses, lasers and even Star Trek-like cloaking materials are possible.
“This work shows that nanoparticle crystals of extraordinary complexity are possible with DNA technology, once one begins to exploit particle shape,” said Sharon C. Glotzer, the John W. Cahn Distinguished University Professor of Engineering and the Stuart W. Churchill Collegiate Professor of Chemical Engineering at U-M. “And, it’s a great example of what can be achieved by experimentalists and simulators teaming up.”
The study, titled “Clathrate Colloidal Crystals,” will be published March 3 in the journal Science. Mirkin and Glotzer are co-corresponding authors of the paper.
In chemistry, clathrates are known for their chambers that can house small molecules. They have been used for capturing pollutants from the environment, for example. The nanoparticle clusters also leave room for cargo, which the authors suggest could be useful for storing, delivering and sensing materials for environmental, medical diagnostic and therapeutic applications.
While natural materials exhibit a dizzying array of crystal structures, most nanotechnology labs struggle to get past simple designs. The structures produced by Haixin Lin, now a postdoctoral fellow in Mirkin’s lab, are far more interesting. The new structures are composed of clusters of up to 42 particles, forming larger polyhedral, such as the great dodecahedron. These clusters connect into cage-like crystal structures called clathrates.
Still, the story isn’t the crystal itself: it’s how the crystal came to be. Mirkin’s group has pioneered many structures through the use of DNA strands as a sort of smart glue, linking nanoparticles together in a particular way. The particle is both a building block and a template that directs bonding interactions. Meanwhile, Glotzer’s group has championed the role of nanoparticle shape in guiding the assembly of crystal structures through computer simulation.
“Chad’s group got the idea of exploring new phases by looking at predictions we had made,” Glotzer said. “One day, I got a phone call from him. ‘We just got these incredible structures!’ he said. And he texted me micrograph after micrograph -- they just kept popping up. He said, we need to figure out a way to definitively assign their structures.”
The electron microscope images, or micrographs, showed complex crystalline structures that formed in large part thanks to the shape of the gold nanoparticles. The triangular bipyramidal shape, like two flattened tetrahedrons stuck together at their bases, was similar to a shape Glotzer’s group predicted would form a quasicrystal. Quasicrystals are prized in the field of nanoassembly because they are as complex as crystals get.
Lin’s shape had just the right angles to make clathrate structures, which often turn up in molecular systems that form quasicrystals. But to do so, they needed strands of DNA attached to their sides at just the right length.
Lin systematically made the gold bipyramids of consistent size and shape, with edge lengths of 250 nanometers -- half the wavelength of blue light. He then modified them with different length sequences of DNA. When the DNA strands were too short, the nanoparticles made disordered, ill-defined structures.
When longer strands produced exotic patterns in the electron microscope images, Lin brought the results to Mirkin, who was both thrilled and intrigued.
“These are stunning -- no one has made such structures before,” said Mirkin, director of Northwestern’s International Institute for Nanotechnology.
It was clear they had made phases never observed before, but getting the structure accurately identified was essential. After Mirkin alerted Glotzer at U-M, Sangmin Lee and Michael Engel 3-D printed Lin’s bipyramids and glued them together to explore how they might make the structures in the electron micrographs. Lee is a doctoral student in chemical engineering, and Engel was then an assistant research scientist, both in Glotzer’s group.
Once they saw how the shapes fit together, they hypothesized the clathrate structures. To confirm their suspicions, they built a computer model of the hypothesized clathrates from bipyramids and compared it to the Northwestern micrographs. It was a perfect match.
As a definitive test, Lee and Matthew Spellings, also a doctoral student in chemical engineering at U-M, developed a molecular model of the DNA-linked nanoparticles. Lee carried out simulations to confirm that the particles would indeed form clathrate structures.
“To really know for sure, we had to run simulations that mimicked the conditions Haixin used in the lab to see if a disordered fluid of DNA-linked bipyramids would assemble into the Northwestern crystals,” Glotzer said. “Once we saw the computer crystals, I knew we had nailed it.”
Mirkin is director of the research group that invented the chemistry for conjugating DNA and nanoparticles and a pioneer of the concept of programmable colloidal crystallization with nucleic acids. In 1996, he introduced the concept of using nanoparticles as atoms and synthetic DNA -- the blueprint of life -- as a chemically programmable bond to make designer materials based upon the ability of the particles to recognize one another through sequences immobilized on their surfaces. Mirkin has been experimentally studying the role of particle shape in colloidal crystal formation for the past two decades. He is also a professor of medicine, chemical and biological engineering, biomedical engineering, and materials science and engineering.
Glotzer is nationally recognized for groundbreaking computer simulations demonstrating the important role of shape in nanoparticle self-assembly. She leads the research group that discovered the enormous diversity and complexity of colloidal crystals possible from simple polyhedral shapes. Glotzer is also a professor of material science and engineering, macromolecular science and engineering, and physics.
The study was supported as part of the Center for Bio-Inspired Energy Science, an Energy Frontier Research Center funded by the U.S. Department of Energy (grant no. DE-SC0000989).
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
MEDIA CONTACTS:
Megan Fellman
Northwestern University
847-491-3115
Katherine McAlpine
University of Michigan
734-763-4386
Chad Mirkin
847-414-4623
Sharon Glotzer
734-615-6296
Copyright © Northwestern University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Crystallography
![]() First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
First measurement of electron energy distributions, could enable sustainable energy technologies June 5th, 2020
![]() How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
How to trick electrons to see the hidden face of crystals: Researchers try a trick for complete 3D analysis of submicron crystals August 3rd, 2019
![]() 3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments June 29th, 2017
3-D-printed jars in ball-milling experiments June 29th, 2017
![]() Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
Novel nozzle saves crystals: Double flow concept widens spectrum for protein crystallography March 17th, 2017
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Self Assembly
![]() Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
Liquid crystal templated chiral nanomaterials October 14th, 2022
![]() Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
Nanoclusters self-organize into centimeter-scale hierarchical assemblies April 22nd, 2022
![]() Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
Atom by atom: building precise smaller nanoparticles with templates March 4th, 2022
![]() Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanostructures get complex with electron equivalents: Nanoparticles of two different sizes break away from symmetrical designs January 14th, 2022
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Environment
![]() Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Billions of nanoplastics released when microwaving baby food containers: Exposure to plastic particles kills up to 75% of cultured kidney cells July 21st, 2023
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








