Home > Press > 2-D material a brittle surprise: Rice University researchers finds molybdenum diselenide not as strong as they thought
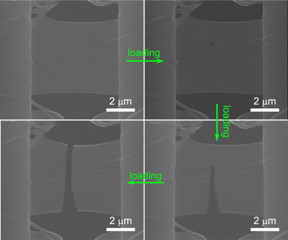 |
| A sequence shows a molybdenum diselenide sample mounted on a nanomechanical measuring device at Rice University, where scientists determine the material is far more brittle than they expected. The atom-thick material is progressively stretched in the photos, clockwise from top left, until it completely splits. The researchers suspect defects as small as a single atom are the starting point for the brittle behavior. Credit: Lou Group/Rice University |
Abstract:
Scientists at Rice University have discovered that an atom-thick material being eyed for flexible electronics and next-generation optical devices is more brittle than they expected.
2-D material a brittle surprise: Rice University researchers finds molybdenum diselenide not as strong as they thought
Houston, TX | Posted on November 14th, 2016The Rice team led by materials scientist Jun Lou tested the tensile strength of two-dimensional, semiconducting molybdenum diselenide and discovered that flaws as small as one missing atom can initiate catastrophic cracking under strain.
The team's report appears this month in Advanced Materials.
The finding may cause industry to look more carefully at the properties of 2-D materials before incorporating them in new technologies, he said.
"It turns out not all 2-D crystals are equal," said Lou, a Rice professor of materials science and nanoengineering. "Graphene is a lot more robust compared with some of the others we're dealing with right now, like this molybdenum diselenide. We think it has something to do with defects inherent to these materials."
The defects could be as small as a single atom that leaves a vacancy in the crystalline structure, he said. "It's very hard to detect them," he said. "Even if a cluster of vacancies makes a bigger hole, it's difficult to find using any technique. It might be possible to see them with a transmission electron microscope, but that would be so labor-intensive that it wouldn't be useful."
Molybdenum diselenide is a dichalcogenide, a two-dimensional semiconducting material that appears as a graphene-like hexagonal array from above but is actually a sandwich of metallic atoms between two layers of chalcogen atoms, in this case, selenium. Molybdenum diselenide is being considered for use as transistors and in next-generation solar cells, photodetectors and catalysts as well as electronic and optical devices.
Lou and colleagues measured the material's elastic modulus, the amount of stretching a material can handle and still return to its initial state, at 177.2 (plus or minus 9.3) gigapascals. Graphene is more than five times as elastic. They attributed the large variation to pre-existing flaws of between 3.6 and 77.5 nanometers.
Its fracture strength, the amount of stretching a material can handle before breaking, was measured at 4.8 (plus or minus 2.9) gigapascals. Graphene is nearly 25 times stronger.
Part of the project led by Rice postdoctoral researcher Yingchao Yang required moving molybdenum diselenide from a growth chamber in a chemical vapor deposition furnace to a microscope without introducing more defects. Yang solved the problem using a dry transfer process in place of a standard acid washing that would have ruined the samples.
To test samples, Yang placed rectangles of molybdenum diselenide onto a sensitive electron microscope platform invented by the Lou group. Natural van der Waals forces held the samples in place on springy cantilever arms that measured the applied stress.
Lou said the group attempted to measure the material's fracture toughness, an indicator of how likely cracks are to propagate, as they had in an earlier study on graphene. But they found that pre-cutting cracks into molybdenum diselenide resulted in it shattering before stress could be applied, he said.
"The important message of this work is the brittle nature of these materials," Lou said. "A lot of people are thinking about using 2-D crystals because they're inherently thin. They're thinking about flexible electronics because they are semiconductors and their theoretical elastic strength should be very high. According to our calculations, they can be stretched up to 10 percent.
"But in reality, because of the inherent defects, you rarely can achieve that much strength. The samples we have tested so far broke at 2 to 3 percent (of the theoretical maximum) at most," Lou said. "That should still be fine for most flexible applications, but unless they find a way to quench the defects, it will be very hard to achieve the theoretical limits."
Co-authors of the paper are Rice graduate students Emily Hacopian, Weibing Chen, Jing Zhang and Bo Li, alumna Yongji Gong and Pulickel Ajayan, chair of Rice’s Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering, the Benjamin M. and Mary Greenwood Anderson Professor in Engineering and a professor of chemistry; Xing Li of Rice and Peking University, China; Minru Wen of Tsinghua University, China, and the Georgia Institute of Technology; Wu Zhou of Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Oak Ridge, Tenn.; Qing Chen of Peking University; and Ting Zhu of the Georgia Institute of Technology.
The research was supported by the Air Force Office of Scientific Research, the Welch Foundation, the Department of Energy Office of Basic Energy Sciences, the National Science Foundation and the National Science Foundation of China.
####
About Rice University
Located on a 300-acre forested campus in Houston, Rice University is consistently ranked among the nation’s top 20 universities by U.S. News & World Report. Rice has highly respected schools of Architecture, Business, Continuing Studies, Engineering, Humanities, Music, Natural Sciences and Social Sciences and is home to the Baker Institute for Public Policy. With 3,910 undergraduates and 2,809 graduate students, Rice’s undergraduate student-to-faculty ratio is 6-to-1. Its residential college system builds close-knit communities and lifelong friendships, just one reason why Rice is ranked No. 1 for happiest students and for lots of race/class interaction by the Princeton Review. Rice is also rated as a best value among private universities by Kiplinger’s Personal Finance. To read “What they’re saying about Rice,” go to http://tinyurl.com/RiceUniversityoverview .
Follow Rice News and Media Relations via Twitter @RiceUNews
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
David Ruth
713-348-6327
Mike Williams
713-348-6728
Copyright © Rice University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
![]() Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
Department of Materials Science and NanoEngineering:
![]() George R. Brown School of Engineering:
George R. Brown School of Engineering:
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
2 Dimensional Materials
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Graphene/ Graphite
![]() NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
NRL discovers two-dimensional waveguides February 16th, 2024
Flexible Electronics
![]() Tin selenide nanosheets enables to develop wearable tracking devices December 9th, 2022
Tin selenide nanosheets enables to develop wearable tracking devices December 9th, 2022
Videos/Movies
![]() New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
New X-ray imaging technique to study the transient phases of quantum materials December 29th, 2022
![]() Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
Solvent study solves solar cell durability puzzle: Rice-led project could make perovskite cells ready for prime time September 23rd, 2022
![]() Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Scientists prepare for the world’s smallest race: Nanocar Race II March 18th, 2022
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Optical computing/Photonic computing
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Military
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
What heat can tell us about battery chemistry: using the Peltier effect to study lithium-ion cells March 8th, 2024
![]() New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
New chip opens door to AI computing at light speed February 16th, 2024
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
Researchers’ approach may protect quantum computers from attacks March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








