Home > Press > Cornell researchers create first self-assembled superconductor
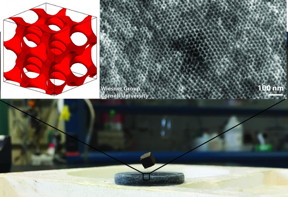 |
| The Wiesner Group at Cornell University has synthesized the first block copolymer self-assembly-derived nanostructured superconductor. Shown is an example of a bismuth-based superconductor levitating a magnet, with simulated and electron microscope images of the nanostructured material. CREDIT: Cornell University |
Abstract:
Building on nearly two decades' worth of research, a multidisciplinary team at Cornell has blazed a new trail by creating a self-assembled, three-dimensional gyroidal superconductor.
Cornell researchers create first self-assembled superconductor
Ithaca, NY | Posted on February 1st, 2016Ulrich Wiesner, a materials science and engineering professor who led the group, says it's the first time a superconductor, in this case niobium nitride (NbN), has self-assembled into a porous, 3-D gyroidal structure. The gyroid is a complex cubic structure based on a surface that divides space into two separate volumes that are interpenetrating and contain various spirals. Pores and the superconducting material have structural dimensions of only around 10 nanometers, which could lead to entirely novel property profiles of superconductors.
Currently, superconductivity for practical uses such as in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanners and fusion reactors is only possible at near absolute zero (-459.67 degrees Fahrenheit), although recent experimentation has yielded superconducting at a comparatively balmy -70 degrees C (-94 degrees F).
"There's this effort in research to get superconducting at higher temperatures, so that you don't have to cool anymore," Wiesner said. "That would revolutionize everything. There's a huge impetus to get that."
Wiesner and his co-author Sol Gruner had been dreaming for over two decades about making a gyroidal superconductor in order to explore how this would affect the superconducting properties. The difficulty was in figuring out a way to synthesize the material. The breakthrough was the decision to use NbN as the superconductor.
Superconductivity, in which electrons flow without resistance and the resultant energy-sapping heat, is still an expensive proposition. MRIs use superconducting magnets, but the magnets constantly have to be cooled, usually with a combination of liquid helium and nitrogen.
Wiesner's group started by using organic block copolymers to structure direct sol-gel niobium oxide (Nb2O5) into three-dimensional alternating gyroid networks by solvent evaporation-induced self-assembly. Simply put, the group built two intertwined gyroidal network structures, then removed one of them by heating in air at 450 degrees.
The team's discovery featured a bit of "serendipity," Wiesner said. In the first attempt to achieve superconductivity, the niobium oxide (under flowing ammonia for conversion to the nitride) was heated to a temperature of 700 degrees. After cooling the material to room temperature, it was determined that superconductivity had not been achieved. The same material was then heated to 850 degrees, cooled and tested, and superconductivity had been achieved.
"We tried going directly to 850, and that didn't work," Wiesner said. "So we had to heat it to 700, cool it and then heat it to 850 and then it worked. Only then."
Wiesner said the group is unable to explain why the heating, cooling and reheating works, but "it's something we're continuing to research," he added.
Limited previous study on mesostructured superconductors was due, in part, to a lack of suitable material for testing. The work by Wiesner's team is a first step toward more research in this area.
"We are saying to the superconducting community, 'Hey, look guys, these organic block copolymer materials can help you generate completely new superconducting structures and composite materials, which may have completely novel properties and transition temperatures. This is worth looking into,'" Wiesner said.
###
The group's findings are detailed in a paper published in Science Advances, Jan. 29.
The work was supported by grants from the National Science Foundation and the U.S. Department of Energy.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Daryl Lovell
607-592-3925
Copyright © Cornell University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Magnetism/Magnons
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
Three-pronged approach discerns qualities of quantum spin liquids November 17th, 2023
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Imaging
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Superconductivity
![]() Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
Optically trapped quantum droplets of light can bind together to form macroscopic complexes March 8th, 2024
![]() 'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
'Sudden death' of quantum fluctuations defies current theories of superconductivity: Study challenges the conventional wisdom of superconducting quantum transitions January 12th, 2024
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chip Technology
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
![]() HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
HKUST researchers develop new integration technique for efficient coupling of III-V and silicon February 16th, 2024
Nanoelectronics
![]() Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
Interdisciplinary: Rice team tackles the future of semiconductors Multiferroics could be the key to ultralow-energy computing October 6th, 2023
![]() Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
Key element for a scalable quantum computer: Physicists from Forschungszentrum Jülich and RWTH Aachen University demonstrate electron transport on a quantum chip September 23rd, 2022
![]() Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
Reduced power consumption in semiconductor devices September 23rd, 2022
![]() Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Atomic level deposition to extend Moore’s law and beyond July 15th, 2022
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Materials/Metamaterials/Magnetoresistance
![]() Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
Nanoscale CL thermometry with lanthanide-doped heavy-metal oxide in TEM March 8th, 2024
![]() Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Focused ion beam technology: A single tool for a wide range of applications January 12th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Tools
![]() Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
Ferroelectrically modulate the Fermi level of graphene oxide to enhance SERS response November 3rd, 2023
![]() The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
The USTC realizes In situ electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy using single nanodiamond sensors November 3rd, 2023
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








