Home > Press > Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks
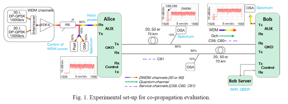 |
| The experimental set-up (Fig. 1) used for the co-propagation evaluation is constituted of a DWDM comb of sixty DP-QPSK (Dual Polarization Quadrature Phase Shift Keying) channels at 100 Gb/s ranged from 1533.6 to 1557 nm (with 50 GHz spacing) and sent to the Aux input (Rx) of the Alice side terminal. CREDIT Orange Innovation division in France |
Abstract:
In a new study, researchers from Orange and Toshiba Europe show that a quantum data channel and classical optical signals can both propagate in the same fiber for several tens of kilometers with a low error rate. The new approach could reduce the cost of implementing quantum key distribution (QKD) for secure data transmission by allowing QKD to be used in already deployed networks.
Researchers demonstrate co-propagation of quantum and classical signals: Study shows that quantum encryption can be implemented in existing fiber networks
Washington, DC | Posted on January 20th, 2023Erwan Pincemin from Orange Innovation division in France will present the new research at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC), which will take place 05 – 09 March 2023 in San Diego.
This work shows that we can have co-propagation of the quantum channel with WDM data channels in the same fiber without changing the engineering rules of the operational WDM links. The high secret key rate obtained in this configuration is very promising for the introduction of QKD in operator’s networks.”, says Paulette Gavignet, senior expert in optical communication at Orange.
QKD uses the quantum properties of light to generate secure random keys for encrypting and decrypting data. Although this approach offers an extremely secure way to encrypt data, widespread deployment has been hampered by the cost and constraints of converting existing networks to QKD-enabled systems. Attempts to transmit quantum signals over existing fiber networks usually suffer from high error rates due to scattering of the co-propagating light.
In the new work, researchers from Orange Innovation division in France and Toshiba Europe Ltd. in the UK evaluated a commercial multiplexed QKD system designed and built by Toshiba. To minimize the effects of scattering, they used a 1310-nm quantum channel to increase the spectral separation between the quantum channel and the QKD service channel as well as the multiplexed data channels. They also added high-extinction spectral filters and time-domain gating at the QKD receiver to isolate the quantum channel from the co-propagating signals and scattered light, which boosted the signal-to-noise ratio. The performance of each communication link was further optimized using automatic self-optimization routines that dynamically adjust various optical parameters.
The researchers tested the QKD system to see if it could be implemented on a wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) link already deployed in the field and to determine how many WDM channels could be mixed with the QKD signal in a standard single-mode fiber. They found that co-propagation of a QKD quantum channel at 1310 nm using 60-channel WDM at 100 Gb/s produced a total data rate of 6 Tb/s. In addition, emission of a secure key with very high aggregated power was possible for both 50 km and 70 km fiber lengths. These results show that a commercial QKD system could be deployed on existing fully filled WDM links with 100 Gb/s and 400 Gb/s channels in data center interconnection applications.
The new results suggested that the number of channels and/or the total bit rate that co-propagate with the quantum channel are not the best parameters for evaluating the ability of classical and QKD channels to co-exist. Instead, the most important parameter was the WDM total power that co-propagates with the quantum channel. With this in mind, the researchers proposed a new figure of merit called co-propagation efficiency for evaluating the performance of classical and QKD signal co-propagation. Based on this metric, they determined that the new QKD implementation outperformed previous co-propagating experiments.
Registration Information
Registration is free for credentialed media and analysts. The registration includes in-person and virtual attendance. Digital assets are available for credentialed media. Learn more: OFC media room.
####
About Optica
Optica (formerly OSA), Advancing Optics and Photonics Worldwide, is the society dedicated to promoting the generation, application, archiving and dissemination of knowledge in the field. Founded in 1916, it is the leading organization for scientists, engineers, business professionals, students and others interested in the science of light. Optica’s renowned publications, meetings, online resources and in-person activities fuel discoveries, shape real-life applications and accelerate scientific, technical and educational achievement. Discover more at: Optica.org
About OFC
The 2023 Optical Fiber Communication Conference (OFC) is the premier conference and exhibition for optical communications and networking professionals. For more than 40 years, OFC has drawn attendees from all corners of the globe to meet and greet, teach and learn, make connections and move business forward. OFC includes dynamic business programming, an exhibition of global companies and high impact peer-reviewed research that, combined, showcase the trends and pulse of the entire optical networking and communications industry. OFC is managed by Optica (formerly OSA) and co-sponsored by IEEE Communications Society (IEEE/ComSoc), IEEE Photonics Society and Optica. OFC 2023, a hybrid conference, will take place 05 – 09 March 2023 in San Diego. Follow @OFCConference, learn more at OFC Community LinkedIn, and watch highlights on OFC YouTube.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Ashley Collier
Optica
Office: 202-416-1419
Copyright © Optica
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Quantum Physics
![]() Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
Beyond silicon: Electronics at the scale of a single molecule January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
![]() Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
Quantum computers simulate fundamental physics: shedding light on the building blocks of nature June 6th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
News and information
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Wireless/telecommunications/RF/Antennas/Microwaves
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Quantum communication
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Discoveries
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Announcements
![]() Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
Decoding hydrogen‑bond network of electrolyte for cryogenic durable aqueous zinc‑ion batteries January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
COF scaffold membrane with gate‑lane nanostructure for efficient Li+/Mg2+ separation January 30th, 2026
Events/Classes
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
Photonics/Optics/Lasers
![]() Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
Metasurfaces smooth light to boost magnetic sensing precision January 30th, 2026
![]() From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
From sensors to smart systems: the rise of AI-driven photonic noses January 30th, 2026
![]() ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
ICFO researchers overcome long-standing bottleneck in single photon detection with twisted 2D materials August 8th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








