Home > Press > Predicting the device performance of the perovskite solar cells from the experimental parameters through machine learning of existing experimental results
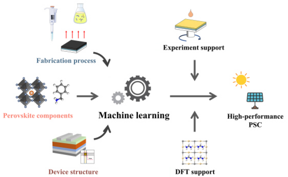 |
| Screening the fabrication process parameters for perovskite solar cells by machine learning. CREDIT Journal of Energy Chemistry |
Abstract:
Metal halide perovskite solar cells (PSCs) have been rapidly developed in the past decade. To obtain high-performance PSCs, it is imperative to optimize the fabrication processes and the composition of the perovskite films. Extensive work has been carried out to determine the effects of the fabrication processes and composition of the perovskite films on the device performance. However, it has been challenging to elucidate their correlations because of the enormous variable space constructed by these factors. Exploring these relations is undoubtedly critical to predict the device performance for efficient device optimization. However, owing to the complexity of these factors, it has been impossible thus far to carry out this work solely through experimentation.
Predicting the device performance of the perovskite solar cells from the experimental parameters through machine learning of existing experimental results
Dalian, China | Posted on November 18th, 2022 constructed by these factors. Exploring these relations is undoubtedly critical to predict the device performance for efficient device optimization. However, owing to the complexity of these factors, it has been impossible thus far to carry out this work solely through experimentation.
Recently, Professor Zheng Xu and Associate Professor Dandan Song of Beijing Jiaotong University adopted the machine learning (ML) approach to explore these correlations by learning the existing experimental results, thereby enabling the prediction of the device performance from these factors. The effects of these factors on the device performance were analyzed by shapley additive explanations (SHAP) analysis. Furthermore, to improve the interpretability of the ML model, the authors considered A-site cations as an example to explain and verify the predicted results by density functional theory (DFT) calculations and experiments. This work thoroughly elucidates how ML guides device optimization, thereby also serving as a guide for the reverse design of experiments to obtain high-performance PSCs.
This research was published in the Journal of Energy Chemistry as “Predicting the device performance of the perovskite solar cells from the experimental parameters through machine learning of existing experimental results.”
####
About Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
About the journal
The Journal of Energy Chemistry is a publication that mainly reports on creative researches and innovative applications of chemical conversions of fossil energy, carbon dioxide, electrochemical energy and hydrogen energy, as well as the conversions of biomass and solar energy related with chemical issues to promote academic exchanges in the field of energy chemistry and to accelerate the exploration, research and development of energy science and technologies.
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Xiaoluan Wei
Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
Office: 86-041-184-379-021
Copyright © Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, Chinese Academy Sciences
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Perovskites
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Energy
![]() Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
Sensors innovations for smart lithium-based batteries: advancements, opportunities, and potential challenges August 8th, 2025
![]() Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Simple algorithm paired with standard imaging tool could predict failure in lithium metal batteries August 8th, 2025
Solar/Photovoltaic
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
KAIST researchers introduce new and improved, next-generation perovskite solar cell November 8th, 2024
![]() Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
Groundbreaking precision in single-molecule optoelectronics August 16th, 2024
![]() Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
Development of zinc oxide nanopagoda array photoelectrode: photoelectrochemical water-splitting hydrogen production January 12th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








