Home > Press > New hybrid structures could pave the way to more stable quantum computers: Study shows that merging a topological insulator with a monolayer superconductor could support theorized topological superconductivity
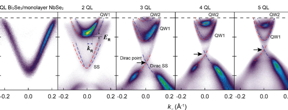 |
| Using a technique known as molecular beam epitaxy, Penn State researchers have synthesized hybrid structures only a few atoms thick that are a good platform for the exploration of an unusual form of superconductivity called topological superconductivity. The structures are composed of a topological insulator Bi2Se3 film and a superconducting NbSe2 monolayer (electronic band structures shown in the top panel) and demonstrate a shift from a kind of superconductivity called Ising-type to a different kind called Rashba-type (bottom panel). Credit: Yi et al. Nature Materials. |
Abstract:
A new way to combine two materials with special electrical properties — a monolayer superconductor and a topological insulator — provides the best platform to date to explore an unusual form of superconductivity called topological superconductivity. The combination could provide the basis for topological quantum computers that are more stable than their traditional counterparts.
New hybrid structures could pave the way to more stable quantum computers: Study shows that merging a topological insulator with a monolayer superconductor could support theorized topological superconductivity
University Park, PA | Posted on October 28th, 2022Superconductors — used in powerful magnets, digital circuits, and imaging devices — allow the electric current to pass without resistance, while topological insulators are thin films only a few atoms thick that restrict the movement of electrons to their edges, which can result in unique properties. A team led by researchers at Penn State describe how they have paired the two materials in a paper appearing Oct. 27 in the journal Nature Materials.
“The future of quantum computing depends on a kind of material that we call a topological superconductor, which can be formed by combining a topological insulator with a superconductor, but the actual process of combining these two materials is challenging,” said Cui-Zu Chang, Henry W. Knerr Early Career Professor and Associate Professor of Physics at Penn State and leader of the research team. “In this study, we used a technique called molecular beam epitaxy to synthesize both topological insulator and superconductor films and create a two-dimensional heterostructure that is an excellent platform to explore the phenomenon of topological superconductivity.”
In previous experiments to combine the two materials, the superconductivity in thin films usually disappears once a topological insulator layer is grown on top. Physicists have been able to add a topological insulator film onto a three-dimensional “bulk” superconductor and retain the properties of both materials. However, applications for topological superconductors, such as chips with low power consumption inside quantum computers or smartphones, would need to be two-dimensional.
In this paper, the research team stacked a topological insulator film made of bismuth selenide (Bi2Se3) with different thicknesses on a superconductor film made of monolayer niobium diselenide (NbSe2), resulting in a two-dimensional end-product. By synthesizing the heterostructures at very lower temperature, the team was able to retain both the topological and superconducting properties.
“In superconductors, electrons form ‘Cooper pairs’ and can flow with zero resistance, but a strong magnetic field can break those pairs,” said Hemian Yi, a postdoctoral scholar in the Chang Research Group at Penn State and the first author of the paper. “The monolayer superconductor film we used is known for its ‘Ising-type superconductivity,’ which means that the Cooper pairs are very robust against the in-plane magnetic fields. We would also expect the topological superconducting phase formed in our heterostructures to be robust in this way.”
By subtly adjusting the thickness of the topological insulator, the researchers found that the heterostructure shifted from Ising-type superconductivity — where the electron spin is perpendicular to the film — to another kind of superconductivity called “Rashba-type superconductivity” — where the electron spin is parallel to the film. This phenomenon is also observed in the researchers’ theoretical calculations and simulations.
This heterostructure could also be a good platform for the exploration of Majorana fermions, an elusive particle that would be a major contributor to making a topological quantum computer more stable than its predecessors.
“This is an excellent platform for the exploration of topological superconductors, and we are hopeful that we will find evidence of topological superconductivity in our continuing work,” said Chang. “Once we have solid evidence of topological superconductivity and demonstrate Majorana physics, then this type of system could be adapted for quantum computing and other applications.”
In addition to Chang and Yi, the research team at Penn State includes Lun-Hui Hu, Yuanxi Wang, Run Xiao, Danielle Reifsnyder Hickey, Chengye Dong, Yi-Fan Zhao, Ling-Jie Zhou, Ruoxi Zhang, Antony Richardella, Nasim Alem, Joshua Robinson, Moses Chan, Nitin Samarth, and Chao-Xing Liu. The team also includes Jiaqi Cai and Xiaodong Xu at the University of Washington.
This work was primarily supported by the Penn State MRSEC for Nanoscale Science and also partially supported by the National Science Foundation, the Department of Energy, the University of North Texas, and the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Gail McCormick
Penn State
Office: 814-863-0901
Copyright © Penn State
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Superconductivity
News and information
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Govt.-Legislation/Regulation/Funding/Policy
![]() New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
New imaging approach transforms study of bacterial biofilms August 8th, 2025
![]() Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
Electrifying results shed light on graphene foam as a potential material for lab grown cartilage June 6th, 2025
![]() Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Institute for Nanoscience hosts annual proposal planning meeting May 16th, 2025
Possible Futures
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Chip Technology
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
A 1960s idea inspires NBI researchers to study hitherto inaccessible quantum states June 6th, 2025
![]() Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Programmable electron-induced color router array May 14th, 2025
Quantum Computing
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Japan launches fully domestically produced quantum computer: Expo visitors to experience quantum computing firsthand August 8th, 2025
Discoveries
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Announcements
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
![]() Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
Researchers develop molecular qubits that communicate at telecom frequencies October 3rd, 2025
![]() Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
Next-generation quantum communication October 3rd, 2025
![]() "Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
"Nanoreactor" cage uses visible light for catalytic and ultra-selective cross-cycloadditions October 3rd, 2025
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
Spinel-type sulfide semiconductors to operate the next-generation LEDs and solar cells For solar-cell absorbers and green-LED source October 3rd, 2025
![]() Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Rice membrane extracts lithium from brines with greater speed, less waste October 3rd, 2025
Grants/Sponsored Research/Awards/Scholarships/Gifts/Contests/Honors/Records
![]() Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
Researchers tackle the memory bottleneck stalling quantum computing October 3rd, 2025
![]() New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
New discovery aims to improve the design of microelectronic devices September 13th, 2024
![]() Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Physicists unlock the secret of elusive quantum negative entanglement entropy using simple classical hardware August 16th, 2024
Research partnerships
![]() Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
Lab to industry: InSe wafer-scale breakthrough for future electronics August 8th, 2025
![]() HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
HKU physicists uncover hidden order in the quantum world through deconfined quantum critical points April 25th, 2025
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








