Home > Press > New nano particles suppress resistance to cancer immunotherapy
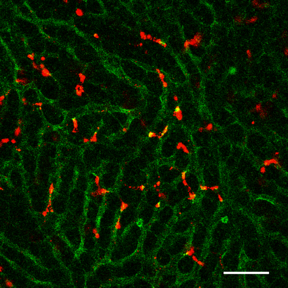 |
| After intravenous injection into mice, STING-lipid nanoparticles (red) transported through blood vessels(green) accumulate in the liver (Takashi Nakamura, et al. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer. July 2, 2021). CREDIT Takashi Nakamura, et al. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer. July 2, 2021. |
Abstract:
A specially designed lipid nanoparticle could deliver immune-signaling molecules into liver macrophage cells to overcome resistance to anti-tumor immunotherapy.
New nano particles suppress resistance to cancer immunotherapy
Hokkaido, Japan | Posted on September 17th, 2021Hokkaido University scientists and colleagues in Japan have found a way that could help some patients overcome resistance to an immunotherapy treatment for cancer. The approach, proven in mice experiments, was reported in the Journal for Immunotherapy of Cancer.
The activation of checkpoint proteins on the surfaces of immune cells help regulate the immune response by preventing them from indiscriminately attacking the body’s other cells. But some cancer cells are able to hijack this mechanism, preventing an immune response against them as well. Scientists have recently developed immune checkpoint inhibitors that can counteract this strategy, but some people are resistant to the treatments.
Now, scientists at Hokkaido University and Aichi Institute of Technology have found a way around this by developing a specially designed lipid nanoparticle that can carry immunity-triggering molecules into immune cells in the liver called macrophages.
The lipid, called YSK12-C4, has a high affinity for immune cells. When intravenously injected into mice with metastatic melanoma, it was able to deliver signaling molecules, called cyclic dinucleotides, across the cell membranes of their liver macrophages, where they stimulated the production of immune-related proteins called type 1 interferons via a stimulator of an interferon gene (STING) pathway. These were released into the blood, activating another type of immune cell called natural killer cells in the spleen and lung, which produced interferon-gamma inside the lung metastases.
This treatment, on its own, only elicited a mild anti-tumor effect. This is because the type 1 interferons and interferon-gamma triggered the expression of a protein called PD-L1 on the cancer cells. PD-L1 prevents a strong tumor-killing immune response of natural killer cells that express PD-1. Administering an anti-PD-1 immunotherapy treatment, however, prevented the cancer cells from turning off those natural killer cells, which then became armed and able to launch a full-scale attack.
“The findings suggest that our lipid nanoparticles carrying immune-signaling molecules convert the immune status from immunologically cold to immunologically hot,” says Takashi Nakamura of Hokkaido University’s faculty of pharmaceutical sciences. “This could lead to the development of a promising adjuvant that reduces resistance to anti-PD-1 antibody treatment in some cancer patients.”
Further studies will need to examine whether the treatment can cause liver toxicity and if different signaling molecules can be used.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Sohail Keegan Pinto
Hokkaido University
Office: +81-11-706-2185
Copyright © Hokkaido University
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related Links |
| Related News Press |
News and information
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
![]() With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
With VECSELs towards the quantum internet Fraunhofer: IAF achieves record output power with VECSEL for quantum frequency converters April 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
Chemical reactions can scramble quantum information as well as black holes April 5th, 2024
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Utilizing palladium for addressing contact issues of buried oxide thin film transistors April 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
NRL charters Navy’s quantum inertial navigation path to reduce drift April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
Simulating magnetization in a Heisenberg quantum spin chain April 5th, 2024
![]() Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Discovery points path to flash-like memory for storing qubits: Rice find could hasten development of nonvolatile quantum memory April 5th, 2024
Nanobiotechnology
![]() New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
New micromaterial releases nanoparticles that selectively destroy cancer cells April 5th, 2024
![]() Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
Good as gold - improving infectious disease testing with gold nanoparticles April 5th, 2024
![]() Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
Researchers develop artificial building blocks of life March 8th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








