Home > Press > Light-emitting tattoo engineered for the first time: Scientists at UCL and the IIT -Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) have created a temporary tattoo with light-emitting technology used in TV and smartphone screens, paving the way for a new type of
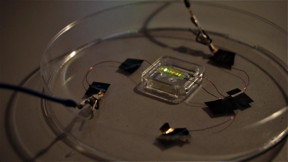 |
| OLED tattoo. CREDIT Barsotti - Italian Institute of Technology. |
Abstract:
Scientists at UCL and the IIT -Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) have created a temporary tattoo with light-emitting technology used in TV and smartphone screens, paving the way for a new type of "smart tattoo" with a range of potential uses.
Light-emitting tattoo engineered for the first time: Scientists at UCL and the IIT -Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (Italian Institute of Technology) have created a temporary tattoo with light-emitting technology used in TV and smartphone screens, paving the way for a new type of
London, UK | Posted on March 4th, 2021The technology, which uses organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), is applied in the same way as water transfer tattoos. That is, the OLEDs are fabricated on to temporary tattoo paper and transferred to a new surface by being pressed on to it and dabbed with water.
The researchers, who described the process in a new paper in the journal Advanced Electronic Materials, say it could be combined with other tattoo electronics to, for instance emit light when an athlete is dehydrated, or when we need to get out of the sun to avoid sunburn. OLEDs could be tattooed on packaging or fruit to signal when a product has passed its expiry date or will soon become inedible, or used for fashion in the form of glowing tattoos.
Professor Franco Cacialli (UCL Physics & Astronomy), senior author of the paper, said: "The tattooable OLEDs that we have demonstrated for the first time can be made at scale and very cheaply. They can be combined with other forms of tattoo electronics for a very wide range of possible uses. These could be for fashion - for instance, providing glowing tattoos and light-emitting fingernails. In sports, they could be combined with a sweat sensor to signal dehydration.
"In healthcare they could emit light when there is a change in a patient's condition - or, if the tattoo was turned the other way into the skin, they could potentially be combined with light-sensitive therapies to target cancer cells, for instance.
"Our proof-of-concept study is the first step. Future challenges will include encapsulating the OLEDs as much as possible to stop them from degrading quickly through contact with air, as well as integrating the device with a battery or supercapacitor."
The OLED device the researchers developed is 2.3 micrometres thick in total (less than one 400th of a millimetre) - about a third of the length of a single red blood cell. It consists of an electroluminescent polymer (a polymer that emits light when an electric field is applied) in between electrodes. An insulating layer is placed in between the electrodes and the commercial tattoo paper.
The light-emitting polymer is 76 nanometres thick (a nanometre is a millionth of a millimetre) and was created using a technique called spin coating, where the polymer is applied to a substrate which is spun at high speed, producing an extremely thin and even layer.
Once they had built the technology, the team applied the tattooable OLEDs, which emitted green light, on to a pane of glass, a plastic bottle, an orange, and paper packaging.
Senior author Professor Virgilio Mattoli, researcher at Italian Institute of Technology said: "Tattoo electronics is a fast-growing field of research. At the Italian Institute of Technology we have previously pioneered electrodes that we have tattooed onto people's skin that can be used to perform diagnostic tests such as electrocardiograms. The advantage of this technology is that it is low-cost, easy to apply and use, and washes off easily with soap and water."
OLEDs were first used in a flatscreen TV 20 years ago. Among the advantages of the technology are that they can be used on flexible, bendy surfaces, and that they can be made from liquid solvents. This means they are printable, providing a cheap way to create bespoke new OLED designs.
####
For more information, please click here
Contacts:
Mark Greaves
44-079-906-75947
@uclnews
Copyright © University College London
If you have a comment, please Contact us.Issuers of news releases, not 7th Wave, Inc. or Nanotechnology Now, are solely responsible for the accuracy of the content.
| Related News Press |
Organic Electronics
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
Display technology/LEDs/SS Lighting/OLEDs
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
News and information
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Possible Futures
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Nanomedicine
![]() The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression July 5th, 2024
The mechanism of a novel circular RNA circZFR that promotes colorectal cancer progression July 5th, 2024
![]() Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
Diamond glitter: A play of colors with artificial DNA crystals May 17th, 2024
![]() Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies May 17th, 2024
Advances in priming B cell immunity against HIV pave the way to future HIV vaccines, shows quartet of new studies May 17th, 2024
Discoveries
![]() Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
Efficient and stable hybrid perovskite-organic light-emitting diodes with external quantum efficiency exceeding 40 per cent July 5th, 2024
![]() A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
A New Blue: Mysterious origin of the ribbontail ray’s electric blue spots revealed July 5th, 2024
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Announcements
![]() New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
New organic molecule shatters phosphorescence efficiency records and paves way for rare metal-free applications July 5th, 2024
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Interviews/Book Reviews/Essays/Reports/Podcasts/Journals/White papers/Posters
![]() Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
Single atoms show their true color July 5th, 2024
![]() New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
New method cracked for high-capacity, secure quantum communication July 5th, 2024
![]() Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
Searching for dark matter with the coldest quantum detectors in the world July 5th, 2024
![]() Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
Atomic force microscopy in 3D July 5th, 2024
|
|
||
|
|
||
| The latest news from around the world, FREE | ||
|
|
||
|
|
||
| Premium Products | ||
|
|
||
|
Only the news you want to read!
Learn More |
||
|
|
||
|
Full-service, expert consulting
Learn More |
||
|
|
||








